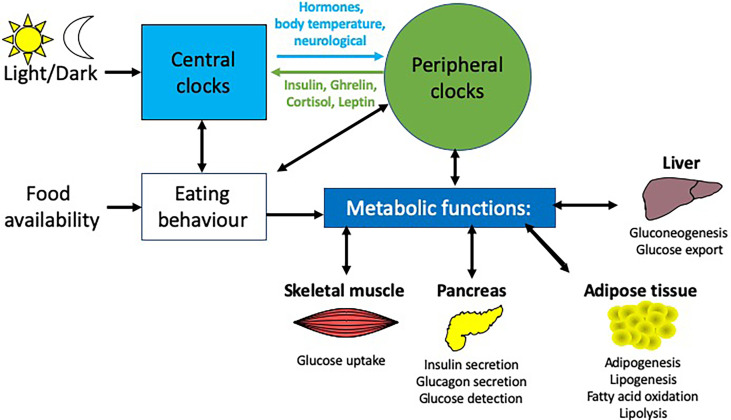
Figure 2.
Circadian influences on different metabolic tissues. Light is the main entrainment factor for the SCN, the master pacemaker of the circadian system, which, through a number of signals e,g. hormones and neurotransmitters, synchronizes the circadian rhythms of peripheral tissues to light exposure. Crosstalk between these peripheral tissues and the brain enable feedback to modulate these rhythms e.g.the hormones insulin, ghrelin, leptin and cortisol provide feedback to the arcuate nucleus in the brain. There are many peripheral tissues, which regulate metabolic functions, including the liver, pancreas, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, each of which exhibit their own rhythmicity. Together, these peripheral rhythms regulate many metabolic functions, including glucose homeostasis, insulin secretion and fatty acid metabolism.