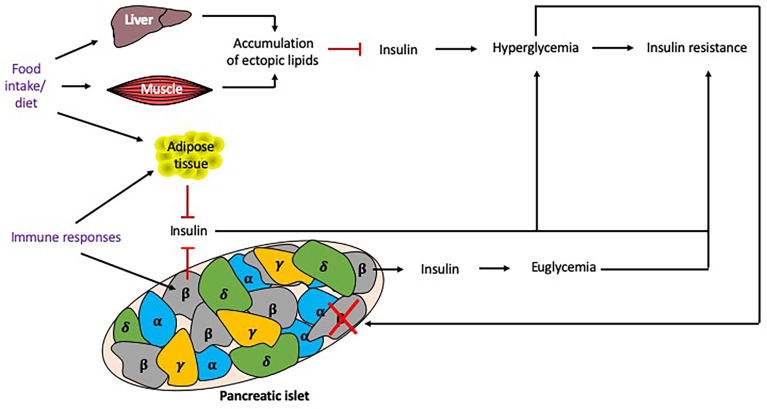
Figure 5.
Factors influencing insulin resistance. Multiple factors may contribute to the development of insulin resistance. Excess food intake and the type of diet eaten can promote the accumulation of lipids in tissues, reducing insulin signaling and causing hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. Chronic hyperglycemia induces β cell stress, leading to β cells that fail to secrete sufficient insulin to maintain euglycemia, or exhausted/destroyed β cells, which do not secrete insulin, further promoting hyperglycemia. Genetics play an important role as some individuals may develop insulin resistance but remain euglycemic. Immune responses, particularly cytokines secreted from macrophages, can also promote adiposity and insulin resistance. Responses to food intake and immune responses (shown in purple) can be altered by the time of day and thus circadian rhythms may alter these responses. Black arrows indicate induction, red lines indicate inhibition.