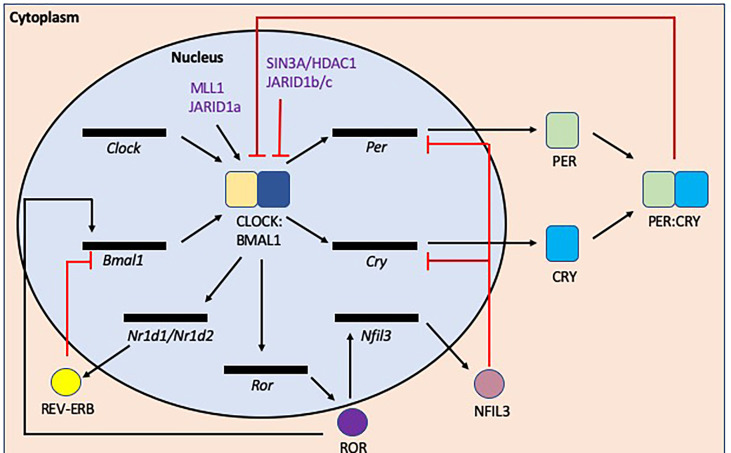
Figure 6.
Transcription/translation feedback loops that modulate circadian rhythms at the molecular level. The induction of circadian rhythms relies on oscillations in gene expression and repression. In the initiation of the circadian rhythms, Bmal1 and Clock are transcribed/translated and then form a heterodimer. This CLOCK : BMAL1 heterodimer initiates the transcription of a number of genes including Per, Cry and Nr1d1/Nr1d2 (rev-erbα/β) genes, all which negatively repress the circadian initiators BMAL1 and/or CLOCK. In addition, CLOCK : BMAL1also activates Ror transcription, promoting transcription of Bmal1, while also inducing Nfil3 transcription/translation, which inhibits Per and Cry gene transcription. There are also epigenetic modulation factors e.g. (de)acetylation or (de)methylation that also regulate the circadian rhythm as shown in purple.