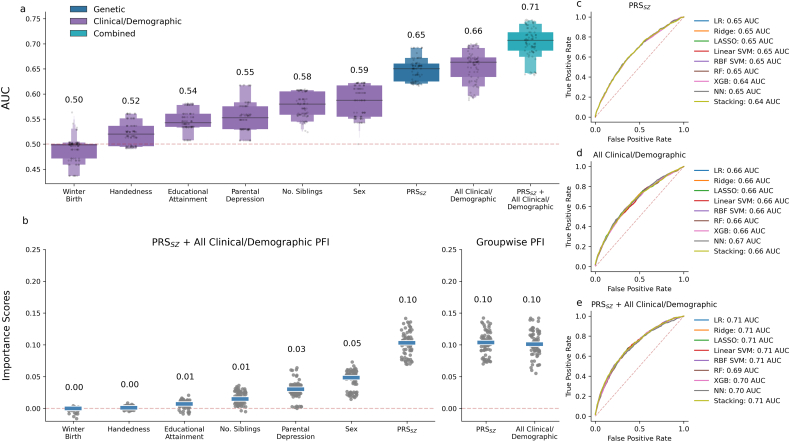
Fig. 2.
Discrimination and importance scores across. Boxen plots of pooled test fold AUROCs from cross-validation for all classifiers show best prediction from combined predictors compared to each predictor individually (a). Median per-predictor permutation feature importance (PFI) scores (b, left) across folds for all classifiers gives sex and schizophrenia polygenic risk score (PRSSZ) as the strongest predictors, while per-group importance (b, right) shows PRSSZ is similar in importance to all clinical and demographic predictors taken together. Importance scores do not indicate direction of effect, for which estimates are given in Appendix B (Table S3). Average receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves show similar average discrimination across classifiers in models using only PRSSZ (c) or all clinical/demographic predictors (d) individually or in combination (e). LR: logistic regression, LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, RF: random forest, SVM: support vector machine, RBF: radial basis function, XGB: XGBoost, NN: neural network.
Discrimination and importance scores across. Boxen plots of pooled test fold AUROCs from cross-validation for all classifiers show best prediction from combined predictors compared to each predictor individually (a). Median per-predictor permutation feature importance (PFI) scores (b, left) across folds for all classifiers gives sex and schizophrenia polygenic risk score (PRSSZ) as the strongest predictors, while per-group importance (b, right) shows PRSSZ is similar in importance to all clinical and demographic predictors taken together. Importance scores do not indicate direction of effect, for which estimates are given in Appendix B (Table S3). Average receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curves show similar average discrimination across classifiers in models using only PRSSZ (c) or all clinical/demographic predictors (d) individually or in combination (e). LR: logistic regression, LASSO: least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, RF: random forest, SVM: support vector machine, RBF: radial basis function, XGB: XGBoost, NN: neural network.