FIG 8.
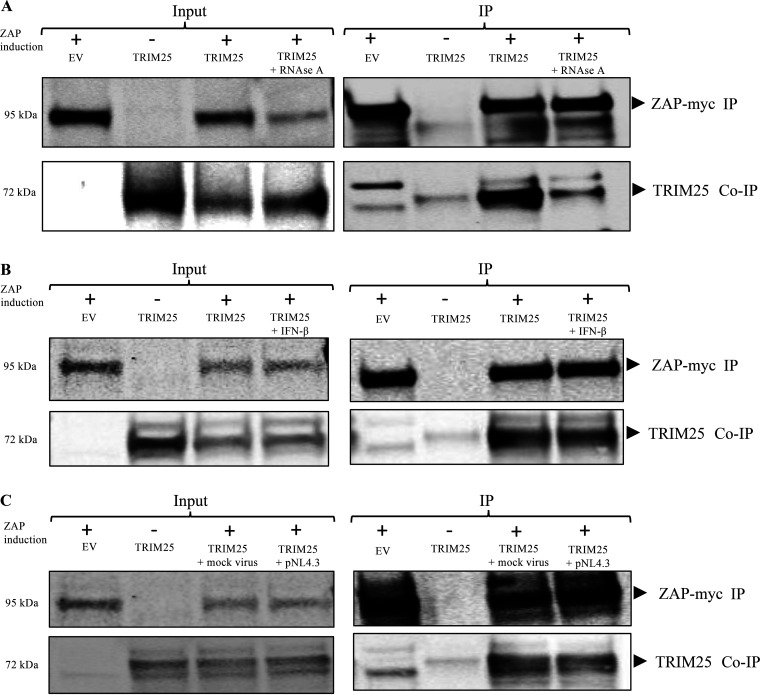
ZAP interaction with TRIM25. (A) ZAP and Trim25 coimmunoprecipitate, and the interaction is RNase sensitive. 293TrexhZAP cells were transfected with an empty vector control (EV) or DNAs expressing the indicated proteins and treated with doxycycline to induce ZAP expression (+) or with DMSO control (−) as indicated. Lysates were prepared 48 h later and treated with RNase as indicated. Lysates were either analyzed directly or subjected to immunoprecipitation for ZAP using a mouse α-myc antibody. (A, Left) In the input data, total proteins in lysate were analyzed by gel electrophoresis, blotted, and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or TRIM25 (bottom). (A, Right) In the IP data, myc-tagged ZAP was recovered by immunoprecipitation using a mouse α-myc antibody, and bound proteins were analyzed by electrophoresis and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or for co-IP of TRIM25 (bottom). Approximate molecular weights of major proteins estimated from size markers are indicated on left. (B) ZAP and TRIM25 co-IP after universal type I interferon treatment. 293TrexhZAP cells were transfected with an EV control or DNAs expressing the indicated proteins and treated with doxycycline to induce ZAP expression (+) or with DMSO control (−) as indicated. Cells were then treated with universal type I interferon at 1,000 U/mL as indicated. Lysates were prepared at 24 h posttransfection and either analyzed directly or subjected to immunoprecipitation for myc-tagged ZAP using a mouse α-myc antibody. (B, Left) In the input data, total proteins in lysate were analyzed by gel electrophoresis, blotted, and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or TRIM25 (bottom). (B, Right) In the IP data, myc-tagged ZAP was recovered by immunoprecipitation using a mouse α-myc antibody, and bound proteins were analyzed by electrophoresis and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or for co-IP of TRIM25 (bottom). Approximate molecular weights of major proteins estimated from size markers are indicated on left. (C) TRIM25 interacts with ZAP in pNL4.3-luc-infected cells. 293TrexhZAP cells were transfected with an EV control or DNAs expressing the indicated proteins and infected with a VSVG-pseudotyped HIV-1luc reporter virus (pNL4.3) or with a mock virus preparation lacking the VSVG envelope (mock virus). Six hours later, cells were treated with dox to induce ZAP expression (+) or with DMSO control (−) as indicated. Lysates were prepared 48 h later and either analyzed directly or subjected to immunoprecipitation for myc-tagged ZAP using a mouse α-myc antibody. (C, Left) In the input data, total proteins in lysate were analyzed by gel electrophoresis, blotted, and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or TRIM25 (bottom). (C, Right) In the IP data, myc-tagged ZAP was recovered by immunoprecipitation using a mouse α-myc antibody, and bound proteins were analyzed by electrophoresis and probed for myc-tagged ZAP (top) or for co-IP of TRIM25 (bottom). Approximate molecular weights of major proteins estimated from size markers are indicated on left.