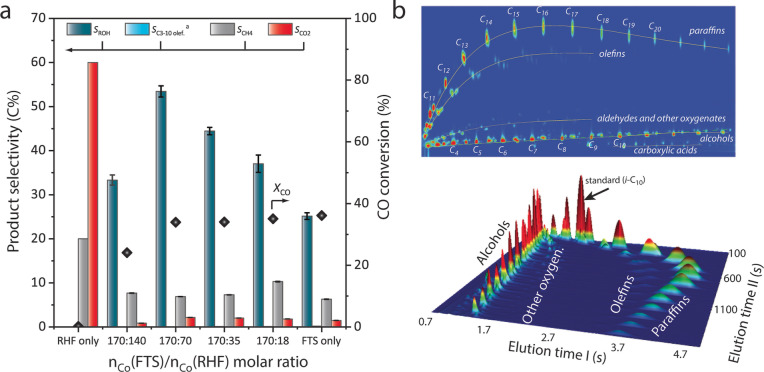
Figure 3.
Direct syngas conversion to higher alcohols via the tandem Fischer–Tropsch synthesis/reductive olefin hydroformylation syngas conversion process. a) Product selectivity (left y‐axis) and CO conversion (right y‐axis) for slurry‐phase tandem FTS/RHF experiments as a function of the n(CoFTS)/n(CoHyFo) catalyst ratios. FTS catalyst: NaPr‐CoRu/AOmM; RHF catalyst: Co2CO8+P(Cy)3 (L : M=1.0 (P/Co (at/at)). The extreme cases, i.e. the FTS and RHF catalysts tested independently, are also included for reference. Reaction conditions: T=473 K, P=120 bar (initial, measured at RT), stirring rate 700 rpm, syngas feed H2:CO=2,2‐methyl pentane as solvent. [a] C3–10 olefin selectivity ≤0.2 C% in all cases. The test with the RHF catalyst alone led to a too low (0.2 %) CO conversion, at which the C balance closed only at 80 %. b) Representative two‐dimensional gas chromatogram for the liquid products in a slurry‐phase FTS/RHF tandem reaction test under optimized reaction conditions.