Figure 2. The OFF pathway cannot drive the PLR or circadian photoentrainment but does drive image-forming vision.
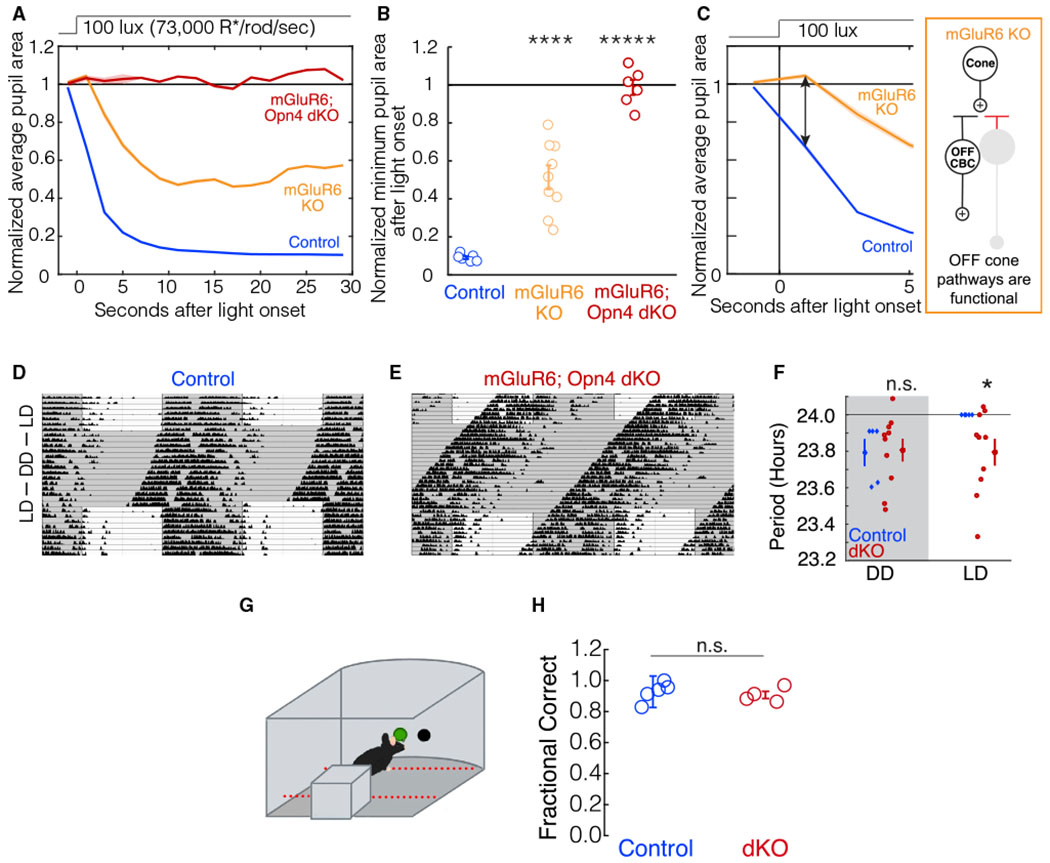
(A) The average pupil constriction over time in response to 100-lux light (73,000 R*/rod/s) beginning at t = 0 s for control (blue, n = 6), mGluR6 KO (orange, n = 9), and mGluR6; Opn4 dKO (dark red, n = 6) mice. Shaded outlines represent SEM. All pupil sizes are normalized to the dark-adapted pupil size (before t = 0).
(B) The minimum normalized pupil area (maximal constriction) in response to 100-lux light from t = 0 to t = 30 s. Individuals are shown as circles. Error bars show SEM. Significance from the littermate control group is as follows: mGluR6 KO, p = 3E–5; mGluR6; Opn4 dKO, p = 3E–6 (ANOVA post hoc Dunnett’s method).
(C) PLR delay seen in (A). mGluR6 KO mice (orange) have a pupil constriction deficit immediately after light onset (ANOVA post hoc Dunnett’s method, p = 0.002). The mGluR6 mutation silences the cone ON pathway in these mice, as indicated by the circuit diagram.
(D) Littermate control mice confine their activity to the dark portions of the 12-h light – 12-h dark (12:12 LD) cycle (n = 5). Light and dark exposure is indicated by white and gray shading.
(E) mGluR6; Opn4 dKO mice do not confine their activity to the dark portions of the day and instead free run in 12:12 LD (n = 10).
(F) Quantification of period lengths from all animals (points indicate individual animals, error bars show SEM). Littermate control mice (blue) photoentrain to the light-dark cycle, as indicated by their period lengths equaling exactly 24 h. mGluR6; Opn4 dKO mice (red) free run in 12:12 LD, as indicated by their period lengths being similar in DD to LD. Littermate control and mGluR6; Opn4 dKO mice have comparable period lengths in DD (Student’s t test, p = 0.90). In 12:12 LD, the mean period lengths of mGluR6; Opn4 dKO mice do not equal 24 h (Student’s one-way t test, p = 0.02). See also Figures S1 and S2.
(G) Schematic depicting the visually guided behavioral task. Mice were trained in the two alternative forced choice paradigm to detect a light stimulus in one of two holes (STAR Methods). The testing chamber was kept dark except for the stimulus presented at photopic levels (28,000 R*/rod/s).
(H) Littermate control mice (blue, n = 5) correctly detect the light stimulus in the visually guided task (G) in ~90% of the trials. mGluR6; Opn4 dKO mice (dark red, n = 4) correctly detect the light stimulus comparable with control mice (Student’s t test, p = 0.59). Error bars indicate SEM.
