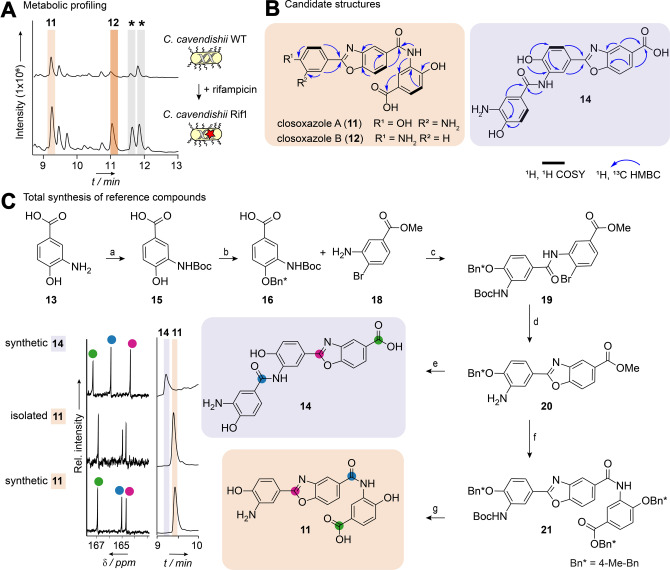
Figure 2.
Isolation and structure elucidation of the closoxazoles. A) HPLC profiles of crude ethyl acetate extracts from cultures of C. cavendishii and C. cavendishii Rif1. Asterisks (*) indicate signals corresponding to putative congeners of closoxazole A. B) Structures with 2D NMR couplings of the main compound 11 and the second candidate structure 14. Compound 12 represents a congener of 11. C) Synthetic route to the reference compounds 11 and 14. a) Dimethylformamide (DMF), Boc2O, 70 °C, 3 h. b) DMF, 4‐methyl benzyl bromide (4‐MeBnBr), K2CO3, then water, then MeOH, NaOH, 70 °C, 4 h then acetic acid. c) Dichloromethane (DCM), N,N‐diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA), then SOCl2, 20 °C, 10 min, then DIPEA, Br‐aniline (18), 20 °C, 12 h. d) CuI, Cs2CO3, phenanthroline, MeCN, microwave. e) DCM, TFA, 65 °C, 3.5 h then MeOH, NaOH. f) DMF, Boc2O, 8 h, then H2O, then MeOH, NaOH, 70 °C, 1 h then HCl, then DCM, DIPEA then SOCl2, 20 °C, 10 min, then DIPEA, 17, 20 °C, 1.5 h. g) DCM, TFA, 70 min, 65 °C. Bn‐protected 17 was synthesized from 15 as follows: DMF, K2CO3, 4‐MeBnBr, 70 °C, then DCM, TFA, 12 h, 40 °C (for details see Supporting Information). HPLC profiles and selected region of 13C NMR spectra of the isolated natural product 11 and both reference compounds 11 and 14.