Figure 4.
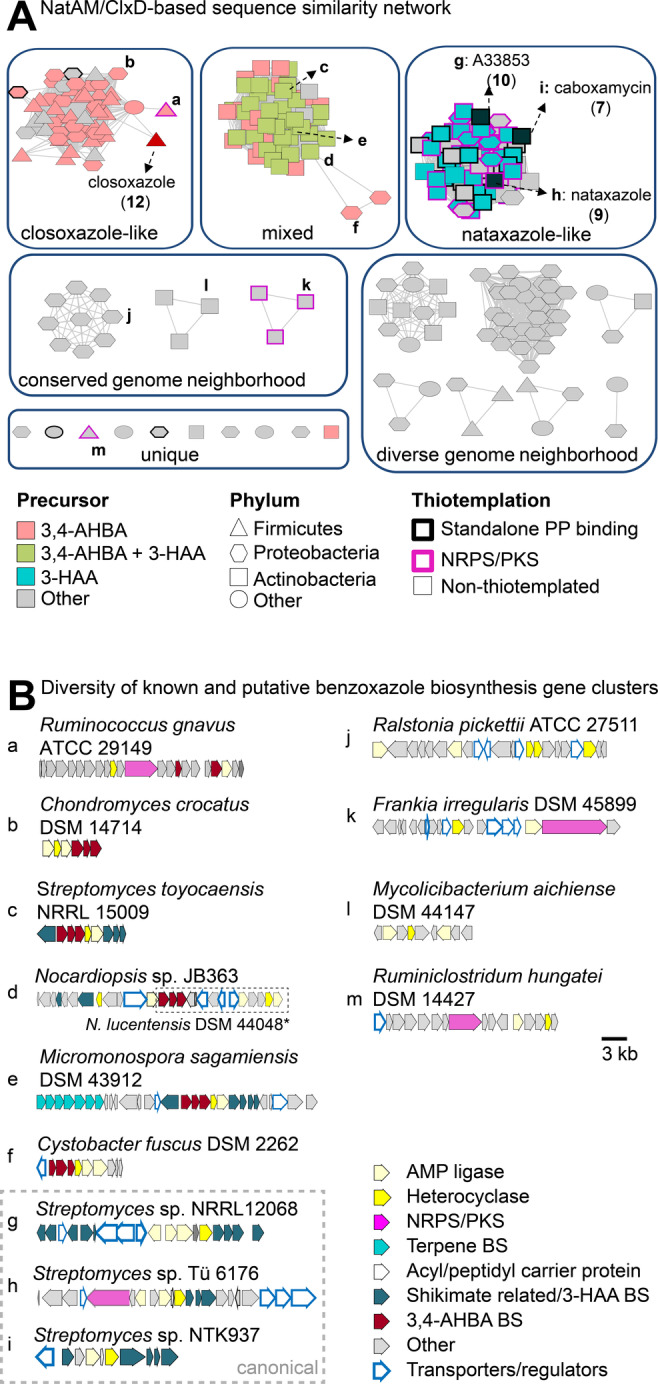
Genome mining for putative benzoxazole biosynthetisis gene clusters. A) Sequence similarity network based on ClxD and NatAM homologs encoded in the vicinity of genes encoding enzymes putatively involved in building block activation. B) Diversity of reported and putative benzoxazole BGCs selected based on architecture diversity and/or ecological or medicinal significance of the potential producer (e.g. R. picketti is an emerging human pathogen and F. irregularis is a plant symbiont). Letters correspond to the node labels in (A). Grey genes marked as “other” also include genes encoding putative tailoring enzymes. The interested reader is directed to the respective protein identifiers in Table S7 to further explore the genome neighborhoods. The conserved subset of genes (noc) in the genome of the nocarbenzoxazole producer N. lucentensis DSM 44048 is highlighted with a dashed box. (*) not represented in sequence similarity network. AMP: adenosine monophosphate. BS: biosynthesis. NRPS: nonribosomal peptide synthetase. PKS: polyketide synthase.
