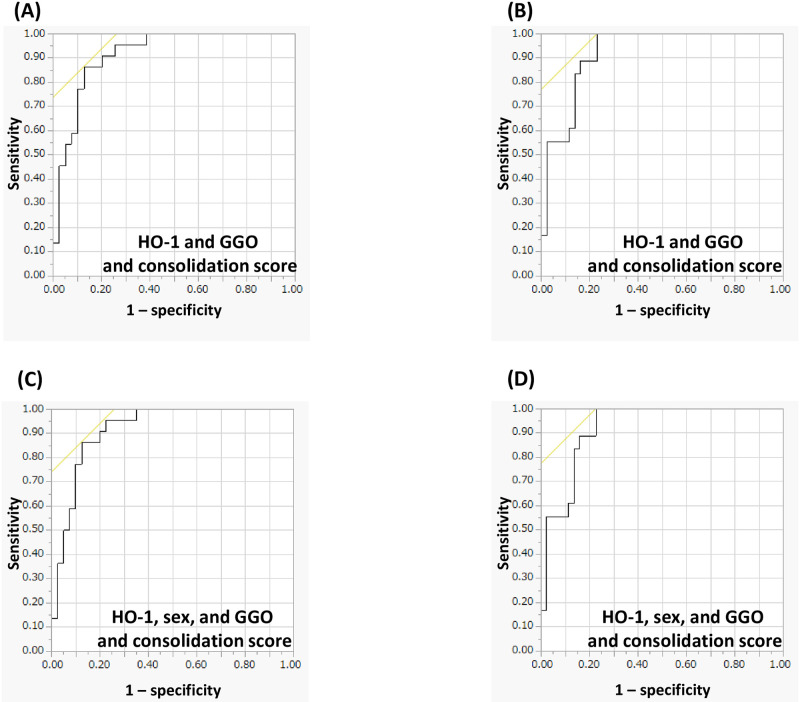
Fig 3. Prediction of treatment outcomes using the combination of serum heme oxygenase (HO)-1 and ground glass opacity (GGO) and consolidation score.
(A) Serum HO-1 and GGO and consolidation score for predicting intensive care unit (ICU) admission: the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC): 0.915 (P < 0.001); (B) Serum HO-1 and GGO and consolidation score for predicting mechanical ventilation: AUC 0.919 (P < 0.001); (C) Serum HO-1, sex, and GGO and consolidation score for predicting ICU admission: AUC 0.916 (P < 0.001); (D) Serum HO-1, sex, and GGO and consolidation score for predicting mechanical ventilation: AUC 0.920 (P < 0.001). (A, C) Analysis of the prediction of ICU admission and mechanical ventilation support using composite parameters including serum HO-1, sex, and the GGO and consolidation score show that the combination has a higher the AUC than the AUCs of a single predictor (only HO-1) or the combination of two (serum HO-1 and GGO and consolidation score). (B, D) The composite parameters including serum HO-1, sex, and the GGO and consolidation score calculated for prediction of mechanical ventilation support shows a higher AUC than AUCs of a single predictor or a combination of two.