Figure 2.
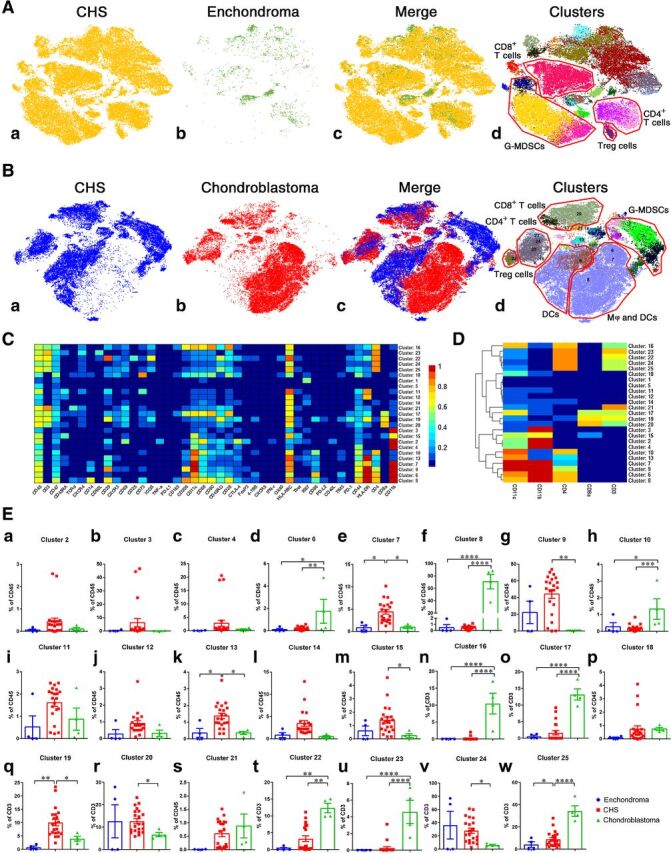
Comparison of intratumoral immune cells among chondrosarcoma, enchondroma, and chondroblastoma. A, t-SNE map showing identified immune-cell subgroups in 21 cases of CHS and 4 cases of enchondromas. The number of intratumoral CD45+ immune cells in enchondromas was very small compared with chondrosarcoma. B, t-SNE map displaying immune-cell phenotypes in CHS and 4 cases of chondroblastomas. Macrophages were almost exclusively seen in chondroblastomas. C and D, Normalized expression of markers for 25 identified immune-cell subgroups from 3 kinds of cartilaginous neoplasms. E, Comparison of clusters among the 3 types of cartilaginous tumors by Bonferroni multiple comparison test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.
