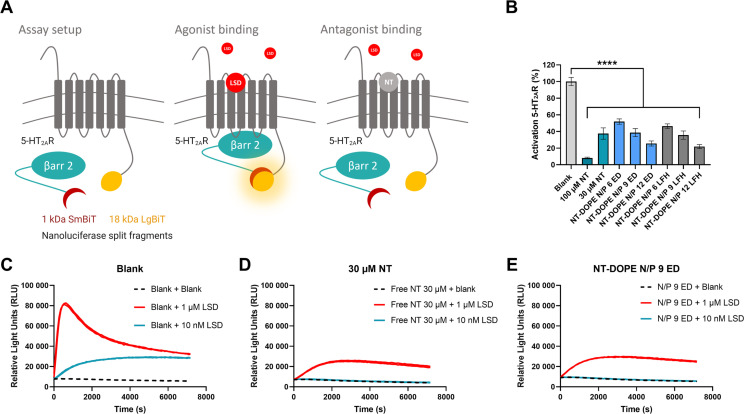
Fig. 4.
Evaluation of the pharmacological activity of nortriptyline following CADosome formulation using a Nanoluciferase Binary Technology (NanoBiT®) bioassay (A) Schematic illustration of the NanoBiT® system, with HEK293T cells stably expressing two inactive luciferase split fragments (1 kDa SmBiT and 18 kDa LgBiT), coupled to the 5-HT2AR (serotonin 2A receptor) and the cytosolic protein β-arrestin 2 (βarr2), respectively [[54], [55], [56]]. Binding of a receptor agonist, in this case LSD, results in βarr2 recruitment to the 5-HT2AR with the concomitant functional complementation of the enzyme, which can be monitored through luminescence read-out. Binding of a receptor antagonist, e.g. nortriptyline (NT), inhibits LSD-induced βarr2 recruitment and subsequent luciferase complementation. (B) Percentage 5-HT2AR activation induced by blank, free NT (30 and 100 μM) and different NT-DOPE CADosomes loaded with eGFP-mRNA, measured by calculating the normalized area under the curve (AUC) values of the receptor activation profiles. 1 μM LSD was added to all samples and luminescence was continuously monitored for 2 h. Data are represented as mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) for three independent repeats (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using One Way Anova with Tukey Correction (**** p ≤ 0.0001). (C–D–E) One representative activation profile of blank, free NT 30 μM and mRNA NT-DOPE N/P 9, respectively.