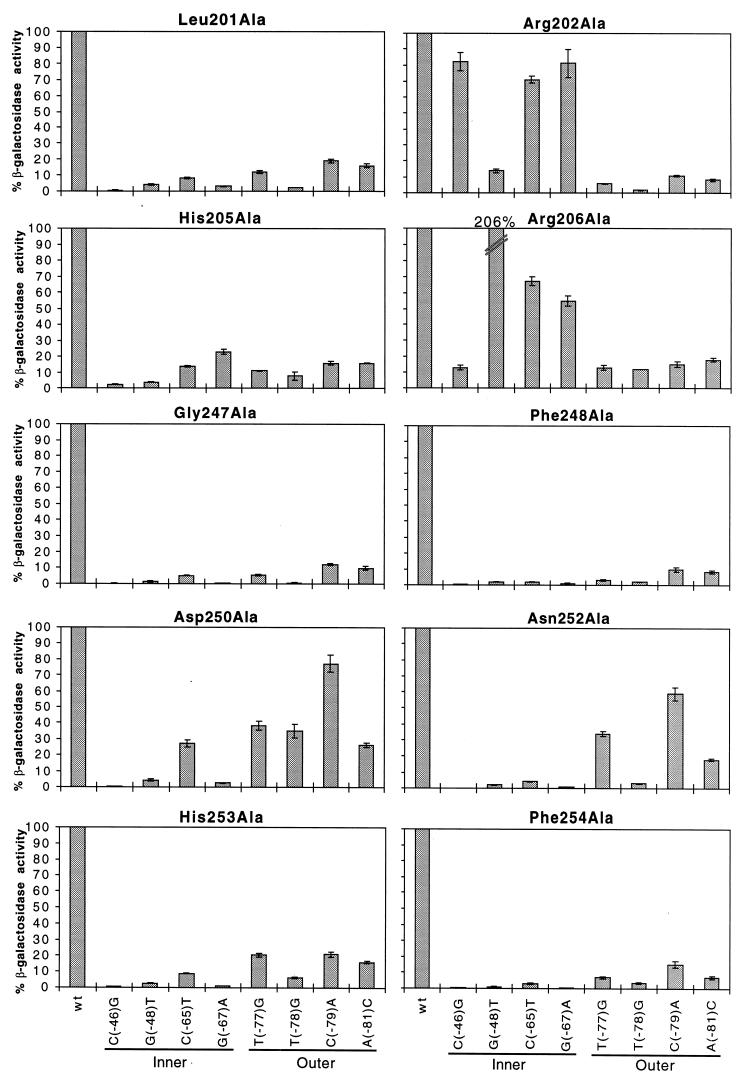
FIG. 3.
Alanine substitutions in RhaS H-T-H 1 and 2 analyzed at mutant rhaB-lacZ fusions. The x axis (labeled at the bottom) represents either the wild-type rhaBAD promoter or the position of point mutations in rhaI found to be important for RhaS binding (Fig. 1). Locations of the point mutations in either the inner or outer major grooves of rhaI are indicated. The y axis (labeled on the left) represents the percent β-galactosidase specific activity for each RhaS alanine mutant at mutant rhaB-lacZ compared with the same mutant protein at the wild-type rhaB-lacZ fusion. The first bar in each graph represents the RhaS alanine mutant protein assayed at the wild-type rhaB-lacZ promoter and is set to 100%. Error bars are shown.