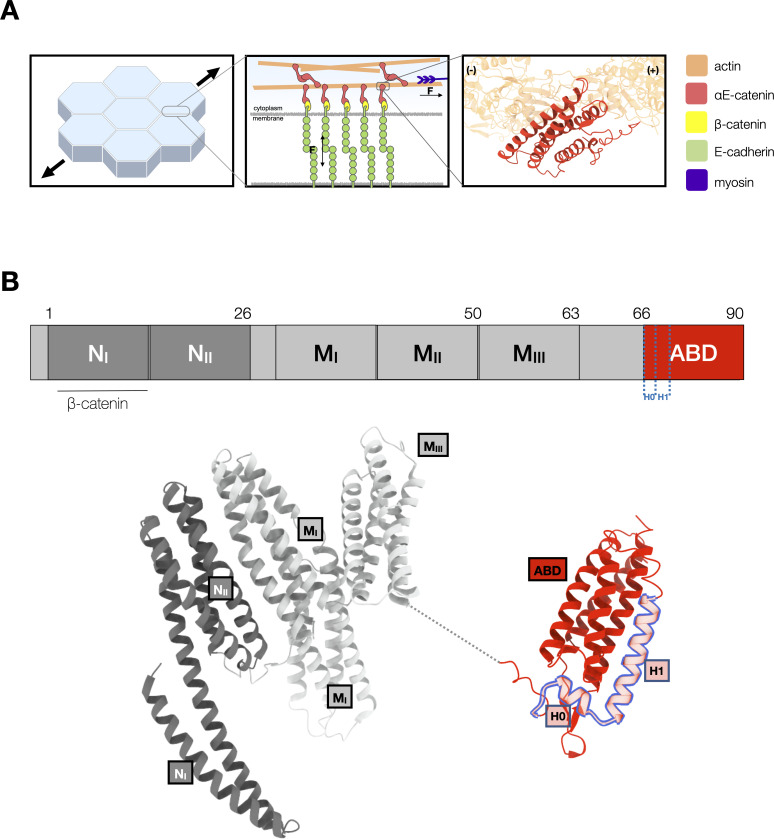
Figure 1. αE-catenin at adherens junctions.
(A) Cell–cell adhesions in epithelia are reinforced under tension. Mechanotransduction at adherens junctions is mediated by both homophilic extracellular E-cadherin (green) interactions that establish adhesion between cells, and intracellular interactions of the cadherin–catenin complex with actin. Intracellularly, the cytosolic tail of E-cadherin binds to β-catenin (yellow) and αE-catenin (red) which forms a catch bond with F-actin. The structure of the αE-catenin actin-binding domain (ABD) complexed with F-actin is the basis for the catch bond mechanistic model. (B) Structure of full-length αE-catenin. αE-catenin (N and M domains: pdb 4igg) has a N-terminal domain that binds β-catenin, a middle (M) domain, and a flexible linker to the C-terminal ABD (pdb 6dv1). The ABD (red) is comprised of a five-helix bundle, preceded by a short N-terminal helix designated as H0, and a C-terminal extension (CTE). Helices H0 and H1 (residues 666–696) are outlined in blue.