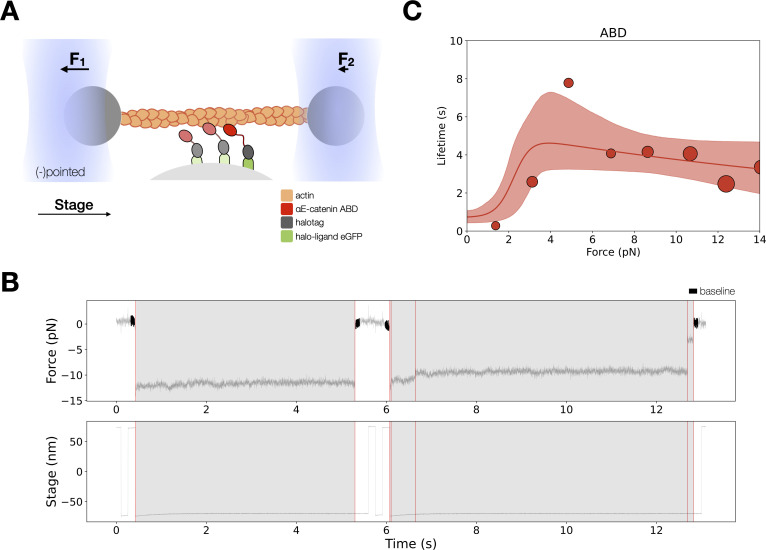
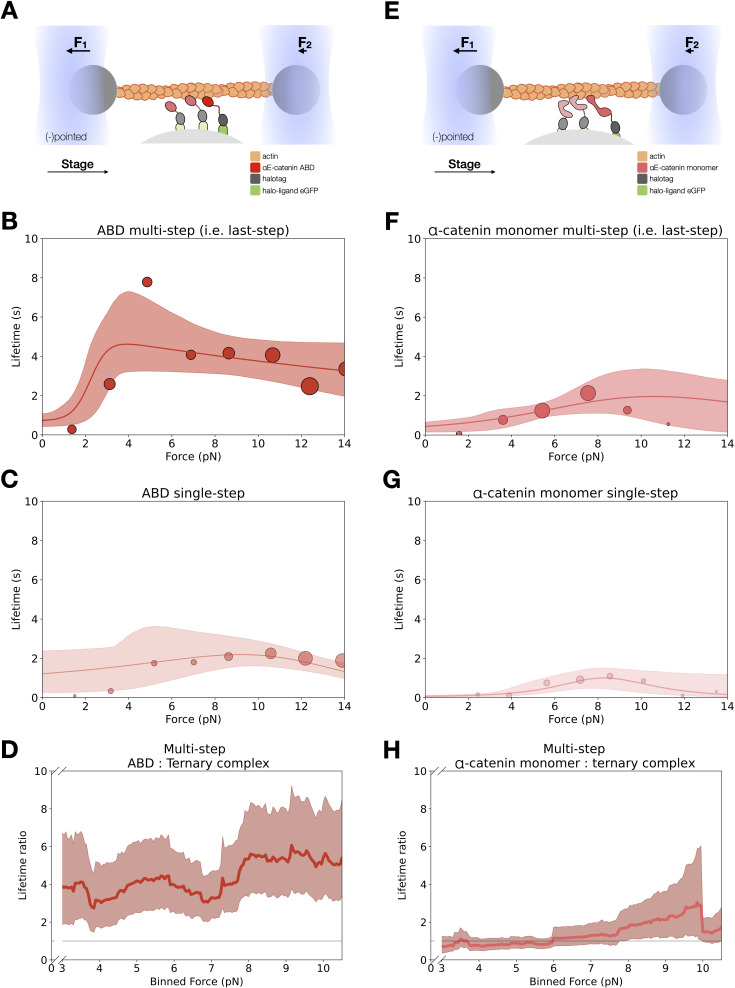
Figure 3. Force-dependent binding interactions between the αE-catenin actin-binding domain (ABD) and F-actin.
(A) (Top) GFP-haloligand and fusion protein Halotag-ABD (red) complexes are immobilized on silica microspheres attached to a microscope coverslip. A taut actin filament is suspended between two optically trapped beads and held over the assembled complexes. The stage is translated parallel to the actin filament, and when at least one protein complex binds to F-actin, the trapped beads are pulled out of their equilibrium position. The restoring force of the optical trap (black arrows) applies tension on a bound complex while bystander complexes (pale) bind and unbind transiently. (B) A representative force versus time series for the constant-force assay. (Top) Plotted are the forces summed from both traps versus time, decimated from 40 to 4 kHz. We observe traces characterized either by rupture of a single bound molecule (left) or by sequential rupture of multiple bound molecules (right). Traces colored in black are regions used for force baseline determination, and vertical lines indicate step boundaries. (Bottom) If summed forces surpass a threshold, stage motion halts until detachment of the final bound molecule. (C) αE-catenin ABD forms a catch bond with F-actin (N = 900). Areas of all circles are proportional to the number of events measured in each equal-width bin. These data are represented here without depicting the direction of force applied relative to the polar actin filament.