Figure 6. Model for cooperative binding under tension.
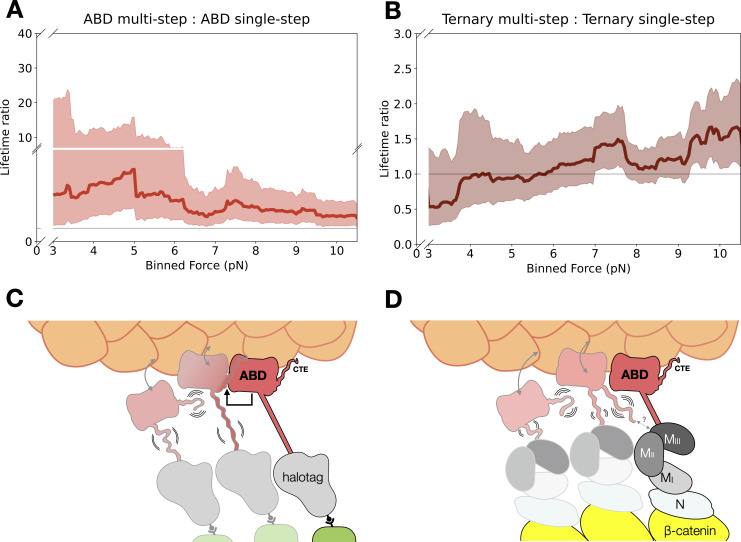
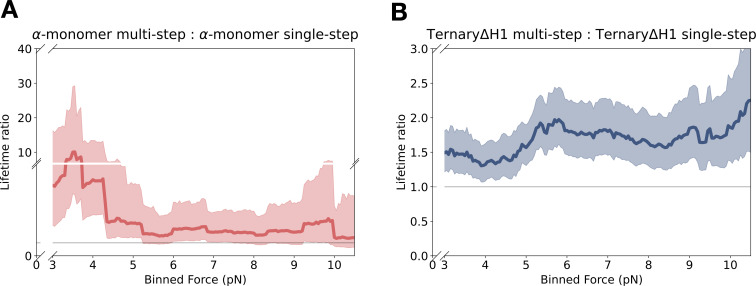
(A) Computed lifetime ratios (LRs) with a 4 pN sliding window across 0–13 pN showing that lifetimes from actin-binding domain (ABD) multi-step events are longer than single-step events (mean LR = 3.54). Envelopes represent 90% confidence intervals (CIs), obtained via empirical bootstrapping mean (90% CI = 1.69–9.83). (B) Wild-type ternary lifetimes from multi- and single-step events have similar binding lifetimes (mean LR = 1.15, 90% CI = 0.68–1.78). (C) Upon stable binding with actin, a loaded ABD could enable stronger binding to actin by neighbors by allosteric coupling of involving contacts of the C-terminal extension (CTE) and the H2–H5 bundle. (D) The loaded ternary complex may interact with its neighbor differently than the ABD. Allosteric regulation of the ABD by the other αE-catenin domains, steric effects of the large N–M region, and/or differences in force propagation could prevent rearrangements in the ABD that would enhance its load-bearing capacity.