Figure 2. Activation of tumor oncogenic pro-growth and survival pathways alters tumor cell susceptibility to T cell CYT.
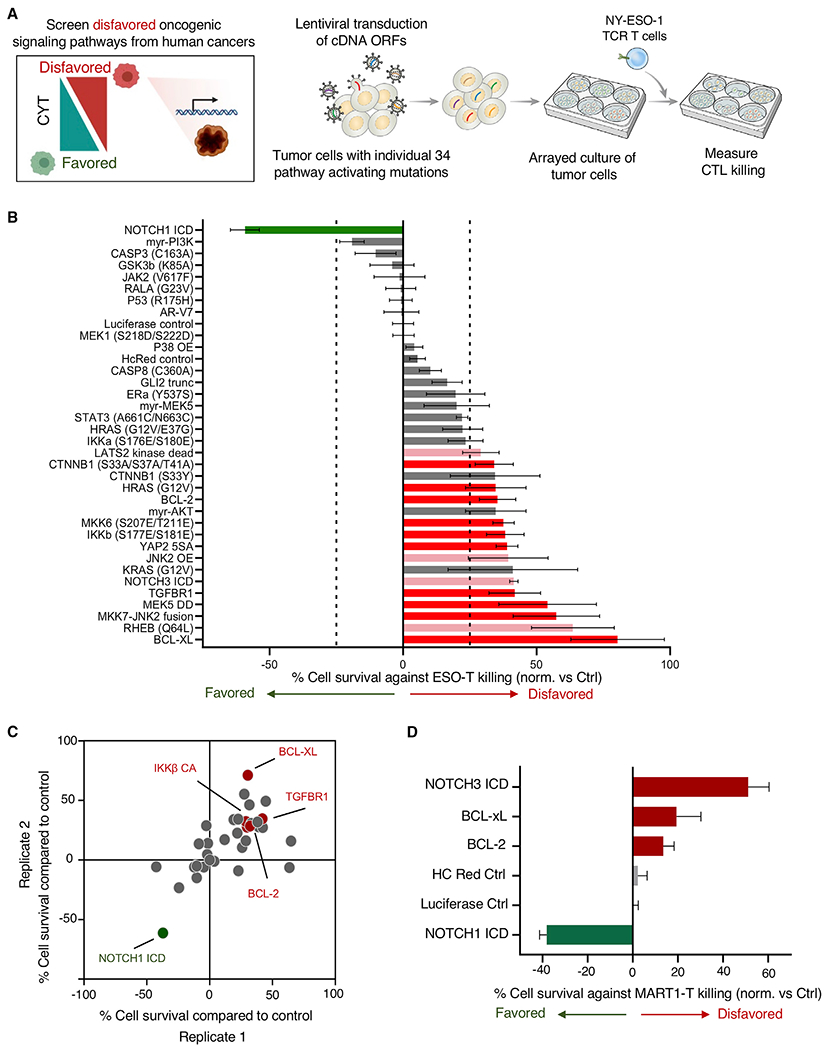
(A) Systematic screening of tumor signaling pathways for potential to alter tumor vulnerability to T cell CYT was performed by transducing A375 melanoma cells with lentiviral cDNA open reading frames (ORFs) encoding proteins driving constitutive activity across pro-growth and survival signaling pathways. Transduced cells were co-cultured with NY-ESO-1 TCR-engineered T cells in an arrayed format, and cytotoxic T cell (CTL) killing of tumor cells was measured.
(B) The impact of each alteration on tumor death after co-culture was determined. Modifications to tumor cells disfavoring T cell killing are shown in red and pink (red depicts modifications found to be statistically significant across 2 independent screens; pink indicates modifications driving statistically significant resistance to killing in 1 screen), and modifications increasing tumor cell killing by T cells are indicated in green. Statistical analysis was performed by 2-tailed Student’s t test, with comparison made to luciferase control. Significant hits were called with p < 0.05. Error bars depict standard deviation.
(C) Results of biological replicate screens are depicted.
(D) Mel624 melanoma cells were transduced with selected pathway activating constructs and susceptibility to MART-1 TCR-engineered T cells was measured. Error bars depict standard deviation.
