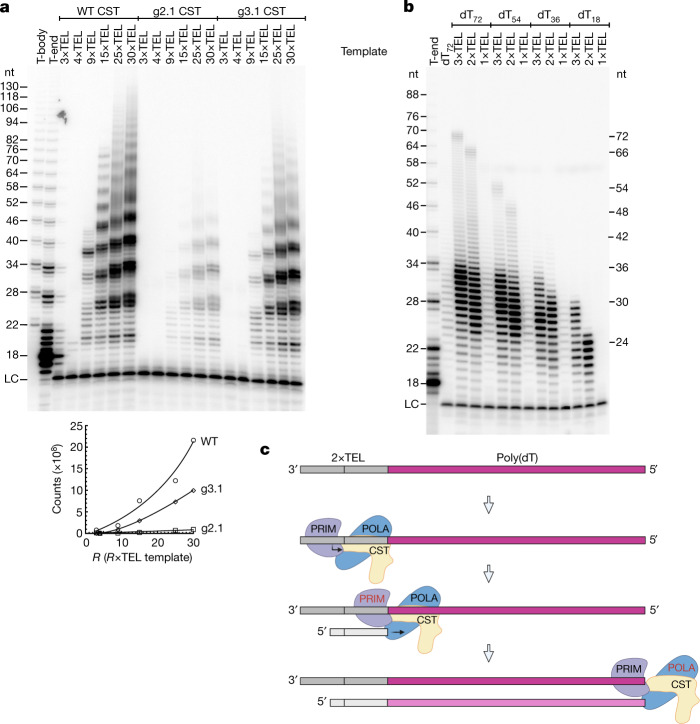
Fig. 2. C-strand synthesis requires DNA binding by CST–Polα–primase, and a CST–Polα–primase-binding site greatly enhances replication of a poly(dT) template.
a, C-strand synthesis for 1 h with DNA templates (100 nM) comprising increasing numbers of telomeric repeats catalysed by WT and two different DNA-binding mutants of CST–Polα–primase (20 nM). The apparent products in the third lane (3×TEL template) are spillover from the adjacent marker lane; repeat experiments confirmed that no product is formed. LC, loading control. Below, quantification of the experiment in a. Total incorporation was normalized to the loading control as a function of the number of telomeric repeats in the template. b, Replication products of CST–Polα–primase on a poly(dT) template, dT72, and on templates with various numbers of telomeric repeats added to the 3′ end of the poly(dT) sequence. c, Model for the initiation of CST–Polα–primase at the telomeric repeats and extension along the template. Whether CST remains bound to Polα–primase during extension is unknown. The length of the rose-coloured C-strand is limited by the template length (shown here) or, for longer templates, by the intrinsic processivity of the enzyme. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.