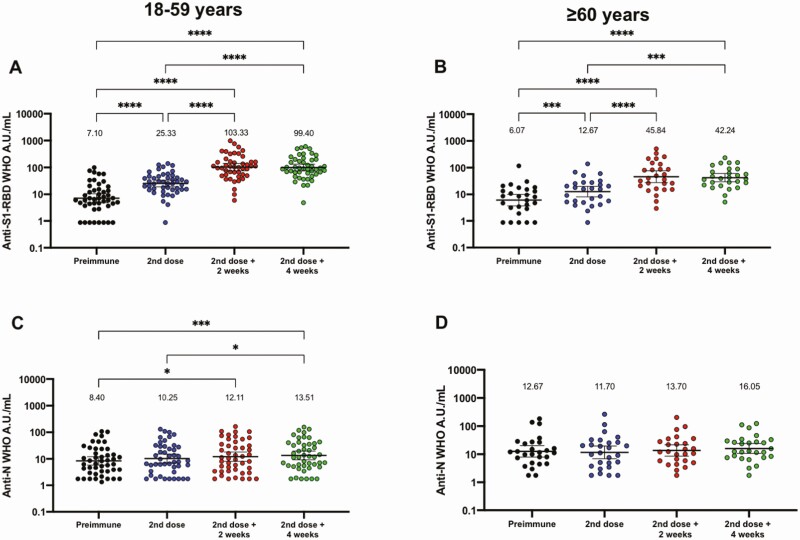
Figure 2.
Immunization with CoronaVac induces specific IgG against SARS-CoV-2 antigens in participants aged 18–59 years and ≥ 60 years after 2 immunizations in a 0–14 schedule. Titers of IgG antibodies after 2 doses of CoronaVac were evaluated for immunized participants (excluding seropositive participants at recruitment and placebo participants) before the first and second dose, and 2 (second dose + 2 weeks) and 4 weeks (second dose + 4 weeks) after the second dose for adults aged (A, C) 18–59 years and (B, D) ≥60 years. Specific IgG against the S1-RBD (upper panel) and the N protein (lower panel) of SARS-CoV-2 were measured. Data are expressed as the log10 of international WHO arbitrary units versus time after each dose. Error bars indicate the 95% CI of the geometric mean units (GMUs). The spots represent the individual values of antibody units for each volunteer, with the numbers above each time showing the GMU estimates. The graph illustrates the results obtained for 45 participants in the 18–59 years group and 27 participants in the ≥60 years group. One-way ANOVAs with repeated measures and post hoc Tukey tests were performed to evaluate statistical differences among the groups; *P < .05, **P < .005, ***P < .0005, ****P < .0001. Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; CI, confidence interval; IgG, immunoglobulin G; N, nucleocapsid; RBD, receptor binding domain; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; WHO, World Health Organization.