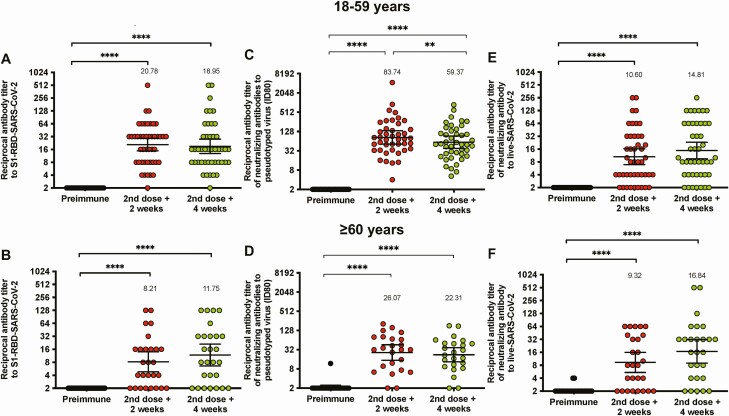
Figure 3.
Immunization with CoronaVac induces neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in participants aged 18–59 years and ≥60 years after 2 immunizations in a 0–14 schedule. (A-B) Neutralizing antibody titers were evaluated with a surrogate virus neutralization assay, which quantifies the interaction between the S1-RBD and hACE2 precoated on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay plates. Results were obtained from (A) 45 participants aged 18–59 years and (B) 27 ≥ 60 years before the first and second dose, and 2 (second dose + 2 weeks) and 4 weeks (second dose + 4 weeks) after the second dose. (C-D) Titers of neutralizing antibodies were evaluated with a pseudotyped viral system. Data are represented as the reciprocal dilution of sera that prevented infection by 80% (ID80) after the first dose. Numbers above the bars show the geometric mean titer (GMT), and the error bars indicate the 95% CI. Results were obtained from 45 participants (C) aged 18–59 years and (D) 24 ≥ 60 years before the first and second dose, and 2 (second dose + 2 weeks) and 4 weeks (second dose + 4 weeks) after the second dose. (E-F) Titers of neutralizing antibodies evaluated with a conventional neutralization assay using an ancestral D614G variant strain of SARS-CoV-2. Data are represented as the reciprocal dilution of sera that prevented infection after the first dose. Numbers above the bars show the GMT, and the error bars indicate the 95% CI. Results were obtained from 45 participants aged (E) 18–59 year and (F) 27 ≥ 60 years before the first and second dose, and 2 (second dose + 2 weeks) and 4 weeks (second dose + 4 weeks) after the second dose. Data are represented as the reciprocal antibody titer versus time after each dose. Numbers above the bars show the GMT, and the error bars indicate the 95% CI. Data were analyzed by a Wilcoxon test to evaluate statistical differences among the groups; *P < .05, **P < .005, ***P < .0005, ****P < .0001. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; RBD, receptor binding domain; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.