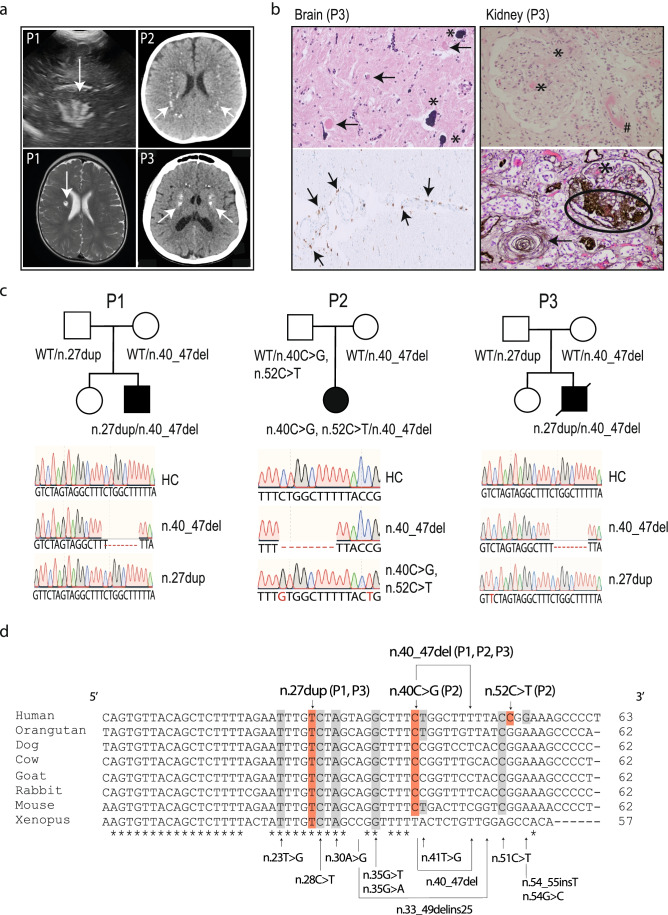
Fig. 1.
AGS patients harboring compound heterozygous RNU7-1 mutations. a Cranial ultrasound of P1 revealed hyperechogenic lines located in the area of lenticulostriate vessels, a radiological image compatible with lenticulostriate vasculopathy (left upper panel). Lenticulostriate ischemic lacunar cerebral infarct on T2-weighted MRI image of P1 (left lower panel). Neuroimaging of P2 and P3 showing spot-like calcifications periventricular and in the basal ganglia on brain CT (right upper and lower panel). b Postmortem histologic examination of brain tissue of P3 revealed numerous calcifications in the walls of arterioles and capillaries (*) with granulovacuolar degeneration of neurons (arrow) adjacent to the affected vessels (left upper panel, 20 ×). Centrum semi-ovale exhibited perivascular crowding of CD68 + activated microglia and histiocytes (left lower panel, 20 ×). Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain of the kidney showed a glomerulus with fibrin thrombi (*) and an arteriole with intramural fibrin precipitation (#) (right upper panel, 200 ×). Silver staining (Jones methenamine) of a glomerulus with mesangiolysis and endothelial swelling (*), segmental sclerosis (oval), and a nearby arteriole with “onion-skinning” (arrow) (right lower panel, 200 ×). c Familial pedigree of patients harboring biallelic mutations in RNU7-1 with electropherograms in comparison to a healthy control (HC). d Clustal Omega alignment of RNU7-1 homologs with mutations of P1, P2, and P3 depicted above (red) and pathogenic variants in RNU7-1 reported to data below (gray) [7]