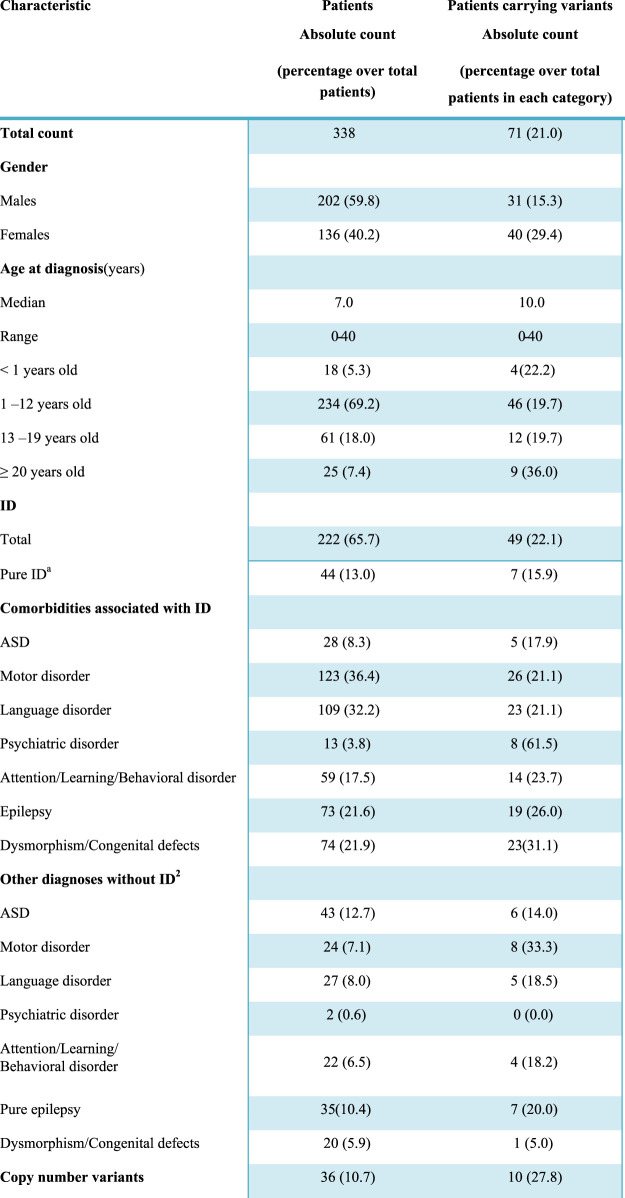
TABLE 1.
Clinical characteristics of the 338 subjects and diagnostic yield.
|
Pure ID, refers to a diagnosis of intellectual disability in the absence of distinct comorbidities such as ASD, attention/learning/behavioral disorders, epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and dysmorphic features. However, considering the high prevalence of motor and language impairment in subjects with ID, these two clinical features were included in the definition.
Each additional diagnosis other than intellectual disability is considered including a potential overlap among the clinical manifestations, so that some patients may have, for instance, ASD, and epilepsy or ASD, and a learning disorder at the same time. Conversely, pure epilepsy is intended here as an isolated clinical entity, i.e. it refers to the presence of symptomatic chronic seizures in the absence of ID, motor or language disorders; ASD, attention/learning/behavioral disorders, psychiatric disorders, or dysmorphic traits.
Abbreviations: ASD, autism spectrum disorder; ID, intellectual disability; LP, likely pathogenic; P, pathogenic.
