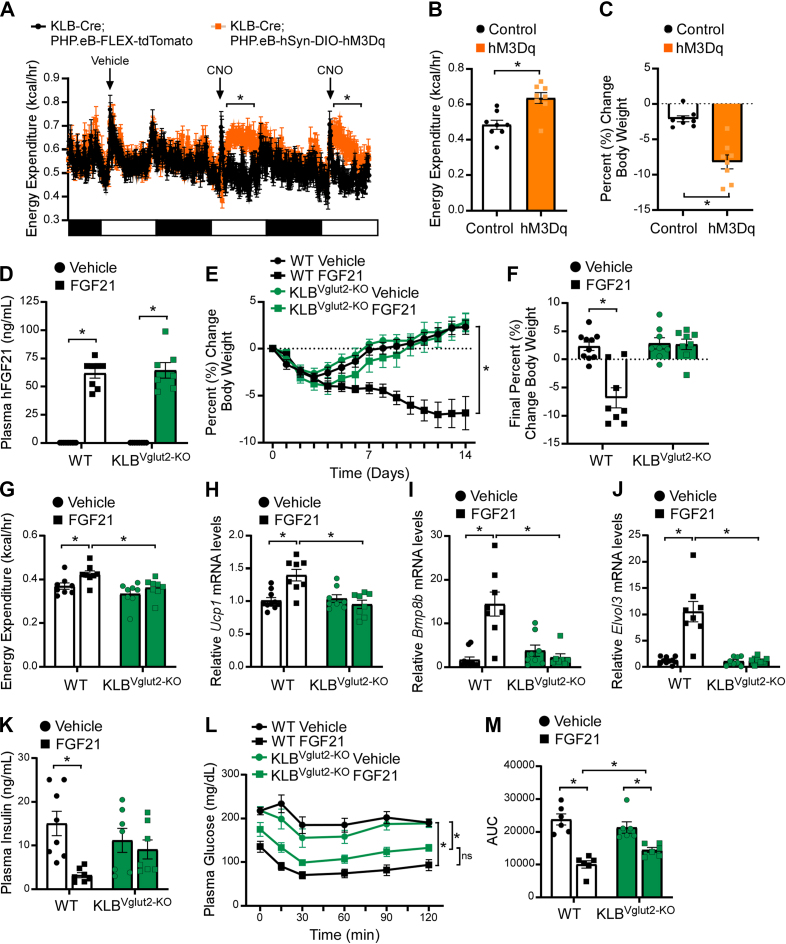
Figure 1.
FGF21 signaling to glutamatergic neurons is required to promote weight loss, but not improve insulin sensitivity, in DIO mice. (A–C) Energy expenditure (A–B) and percent change in body weight (C) in diet-induced obese (DIO) KLB-Cre mice infected with PHP.eB-hSyn-DIO-hM3D (Gq)-mCherry (hM3Dq) or PHP.eB-FLEX-tdTomato (Control) and subsequently treated with vehicle for 2 days followed by CNO (i.p., 1 mg/kg) for 2 days (n = 8/group). (D–F) 16–18 week old DIO WT and KLBVglut2−KO mice were administered vehicle or FGF21 (1 mg/kg/day) by osmotic minipump for 2 weeks (n = 7–10/group). (D) Plasma FGF21 levels, (E) daily percent change in body weight and (F) final percent change in body weight. (G) Energy expenditure in 16–18 week old DIO WT and KLBVglut2−KO mice after 5 days of daily vehicle and 7 days of daily FGF21 injections (i.p., 1 mg/kg) (n = 8/group). (H–K) 16–18 week old DIO WT and KLBVglut2−KO mice were administered vehicle or FGF21 (1 mg/kg/day) by osmotic minipump for 2 weeks (n = 8–10/group). (H–J) Brown adipose tissue mRNA expression of (H) Ucp1, (I) Bmp8b and (J) Elovl3, and (K) plasma insulin levels (n = 7–8/group). (L–M) Plasma glucose levels during an insulin tolerance test (ITT) in DIO WT and KLBVglut2−KO mice at baseline and after 3 weeks of daily FGF21 injections (i.p, 1 mg/kg) (n = 6/group). (M) Quantification of the area under the curve for ITT in (L). Values are mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were conducted using either one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA with Holms-Sidak's multiple comparisons test.