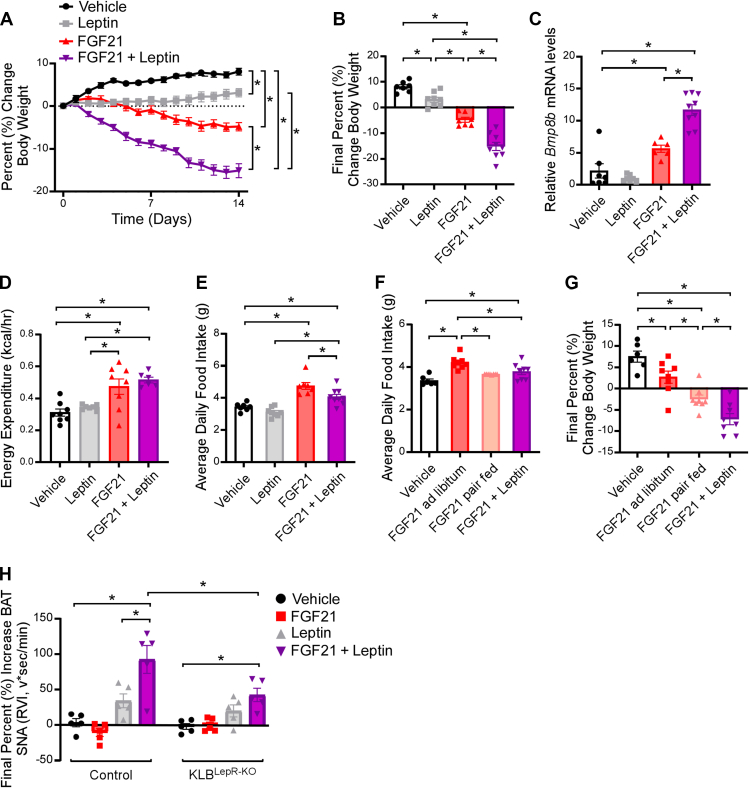
Figure 5.
FGF21 enhances leptin function to reduce body weight. (A–E) 10–12 week old, chow-fed WT mice were administered vehicle, leptin (250 ng/h), FGF21 (1 mg/kg/day) or leptin plus FGF21 by osmotic minipump for 2 weeks (n = 7–9/group). (A) Daily percent change in body weight, (B) final percent change in body weight, (C) Bmp8b mRNA in brown adipose tissue (n = 6–9/group), (D) energy expenditure, and (E) average daily food intake. (F–G) 10–12 week old, chow-fed WT mice were administered vehicle, FGF21 (1 mg/kg/day) or leptin plus FGF21 by osmotic minipumps for 2 weeks (n = 6–8/group). One group of FGF21 treated mice was pair fed to the FGF21 + leptin group. (F) Average daily food intake and (G) final percent change in body weight. (H) Brown adipose tissue sympathetic nerve activity recordings in 11–13 week old, chow-fed WT control or KLBLepR−KO mice administered a single IV injection of vehicle, FGF21 (1 mg/kg), leptin (0.5 μg/g), or FGF21+leptin (n = 5/group). Values are mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were conducted using either one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA with Holms-Sidak's multiple comparisons test.