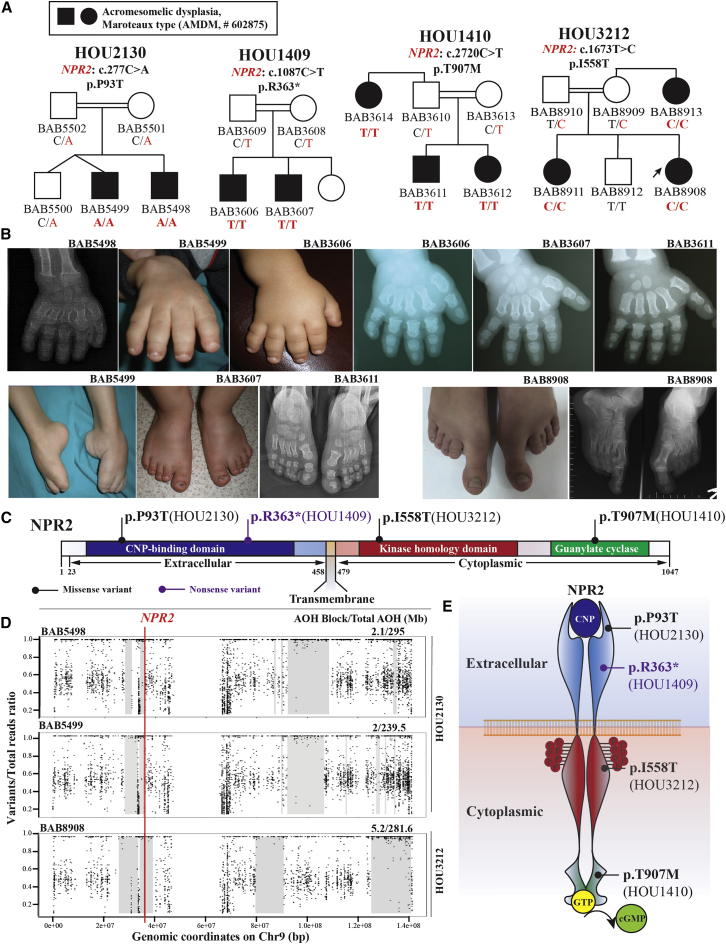
Figure 2.
Biallelic disruption of NPR2 dysregulating longitudinal skeletal growth
(A) Four pedigrees show the segregation of disease-causing variant alleles in each family with AMDM. From left to right: HOU2130 (c.277C>A [p.Pro93Thr]), HOU1409 (c.1087C>T [p.Arg363∗]), HOU1410 (c.2720C>T [p.Thr907Met]), and HOU3212 (c.1673T>C [p.Ile558Thr]).
(B) Clinical images and radiographs from selected individuals with NPR2-related skeletal dysplasia. The top panel shows brachydactyly, nail hypoplasia, and symmetrically short and broad metacarpals and phalanges. From left to right: BAB5498, BAB5499, BAB3606, BAB3607, and BAB3611. The left bottom panel shows similar findings in the feet. From left to right: BAB5499, BAB3607, and BAB3611. The right bottom panel shows a distinct feature in BAB8908, with macrodactyly of halluces with long and wide metatarsals and phalanges of the great toes as well as brachydactyly of other toes because of short metatarsals and phalanges.
(C) A linear protein structure of the transmembrane receptor NPR2, with four identified variant alleles marked in correlated positions (missense variants are labeled as a black line, and a purple line denotes a nonsense variant). Different functional domains and extracellular/cytoplasmic territories of NPR2 are highlighted in different colors.
(D) AOH studies on chromosome 9, visualized by B allele frequency data from personal genomes of two affected individuals in family HOU2130 and proband from family HOU3212. The top two panels for family HOU2130 describe a 2.1 Mb (for BAB5498) and 2 Mb (for BAB5499) interval of AOH genomic interval haplotype block (gray shade) surrounding the causative variant of NPR2 (red vertical line), marked with thick gray rectangles. The bottom panel for HOU3212 denotes a 5.2 Mb AOH interval encompassing the phenotype-associated NPR2 variant allele identified in individual BAB8908.
(E) An illustrative drawing showing the NPR2 homodimer and process of CNP-induced cGMP production. Shown are four identified variant alleles located in different functional domains, and each side of transmembrane territories.