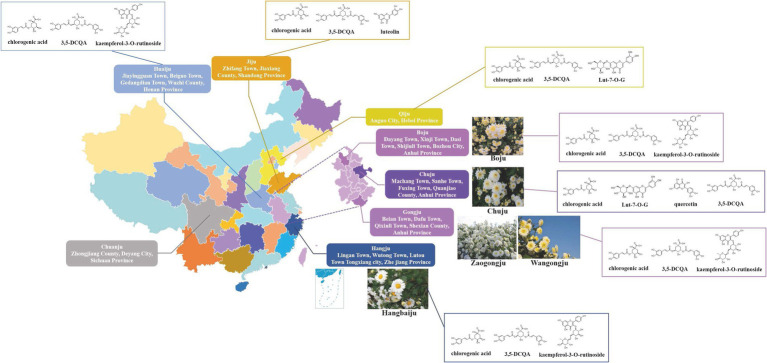
Figure 4.
Geographical distribution, chemical and morphological characteristics of representative CM cultivars. The medicinal quality (Q) markers of each cultivar are shown: Boju, Huaiju, Gongju and Hangju: chlorogenic acid, 3,5-DCQA, and kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (Lu et al., 2022b); Chuju: chlorogenic acid, Lut-7-O-G, quercetin, 3,5-DCQA (Yang et al., 2018b); Qiju: chlorogenic acid, 3,5-DCQA, and Lut-7-O-G (Peng et al., 2019); Jiju: chlorogenic acid, luteolin and 3,5-DCQA (Kang et al., 2022). The Q-marker of Chuanju of Zhongjiang, Sichuan Province is not reported. Morphology of medicinal CM: Boju: Inverted conical or cylindrical shape, sometimes slightly flattened and fan-shaped, 1.5–3 cm in diameter, discrete (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020). Involucral bracts dish-shaped; involucral bracts 3–4 layers, ovate or elliptic, herbaceous, yellow-green or brown-green, pubescent outside, margin membranous. Chuju: Irregular spherical or oblate spherical, diameter 1.5–2.5 cm. Ligulate flowers are white, irregularly twisted, involute, with shriveled edges, sometimes with light brown glandular dots; tubular flowers are mostly hidden. Gongju: Oblate spherical or irregular spherical, 1.5–2.5 cm in diameter. Ligulate flowers white or off-white, obliquely ascending, upper part reflexed, margin slightly involute and shriveled, usually without glandular dots; tubular flowers few, exposed. Hangju: It is dish-shaped or oblate spherical, with a diameter of 2.5–4 cm, and is often connected in several pieces. Ligulate flowers white or yellow, spreading or slightly folded, adhering to each other, usually without glandular dots; tubular flowers numerous, exposed. Huaiju: Irregular spherical or oblate spherical, diameter 1.5–2.5 cm. Ligulate flowers are the most, white or yellow, irregularly twisted, involute, with shriveled edges, and sometimes glandular dots can be seen; most of the tubular flowers are hidden.