Figure 2. Associations of Mean Metabolic Equivalent of Task (MET) Hours per Week of Running, Cycling, Swimming, and Other Aerobic Activities With All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Cancer Mortality.
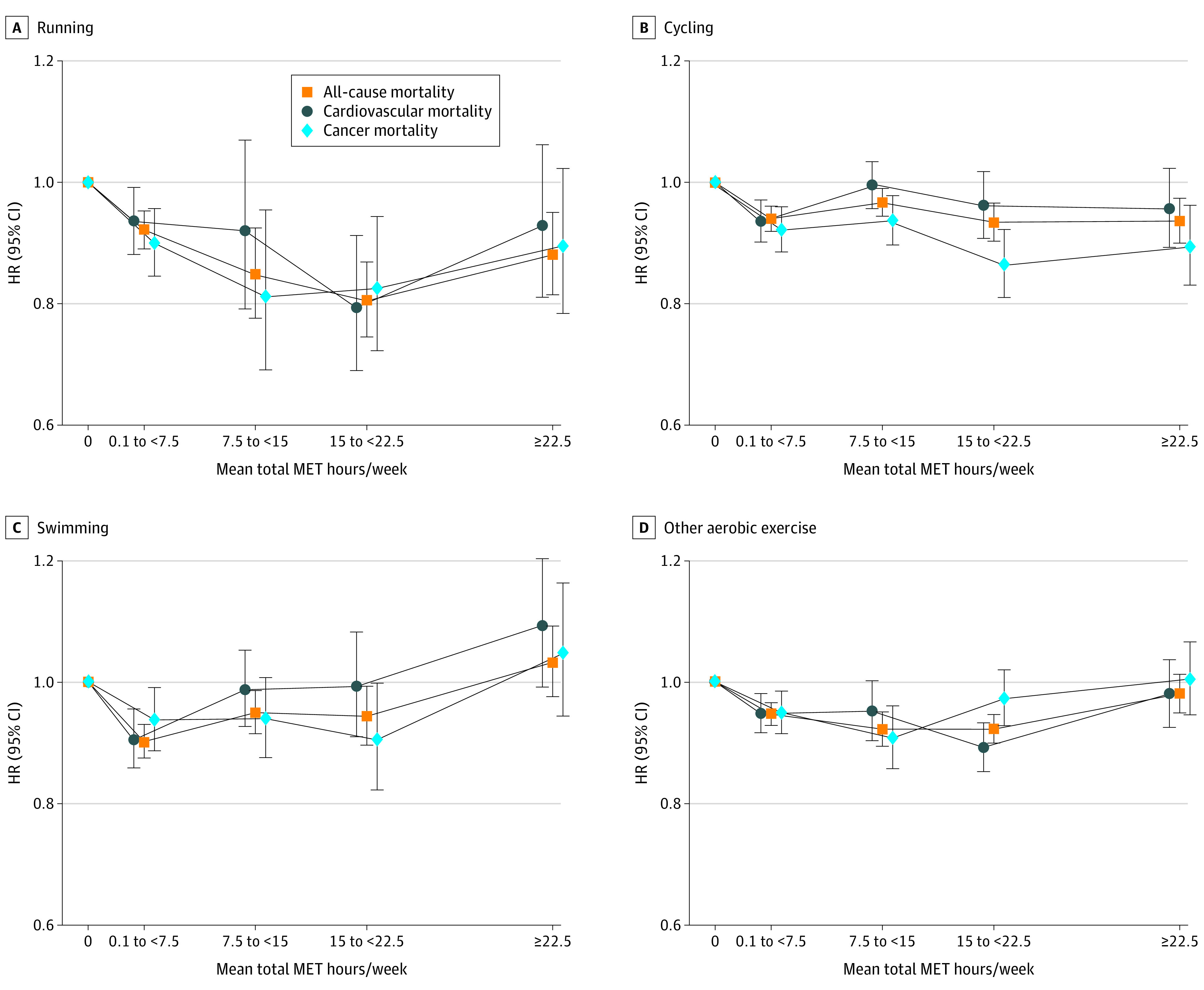
Hazard ratios (HRs) were adjusted for age; sex; racial and ethnic group; educational level; smoking status; body mass index; alcohol consumption; marriage status; trouble with physical activity; history of stroke; history of myocardial infarction, angina, or coronary artery disease; history of diabetes; ever received a diagnosis of cancer; total MET hours per week from nonleisure time activities; sedentary time; weight training frequency; and total MET hours per week from other leisure time activities (excluding the activity of interest). The data points indicate the HRs, and vertical lines indicate 95% CIs. The lines joining the data points are to illustrate the shape of the dose-response association.
