Figure 6. After N. brasiliensis infection, Mo-AMs preferentially express arginase 1, which is dependent on extrinsic neutrophil signaling.
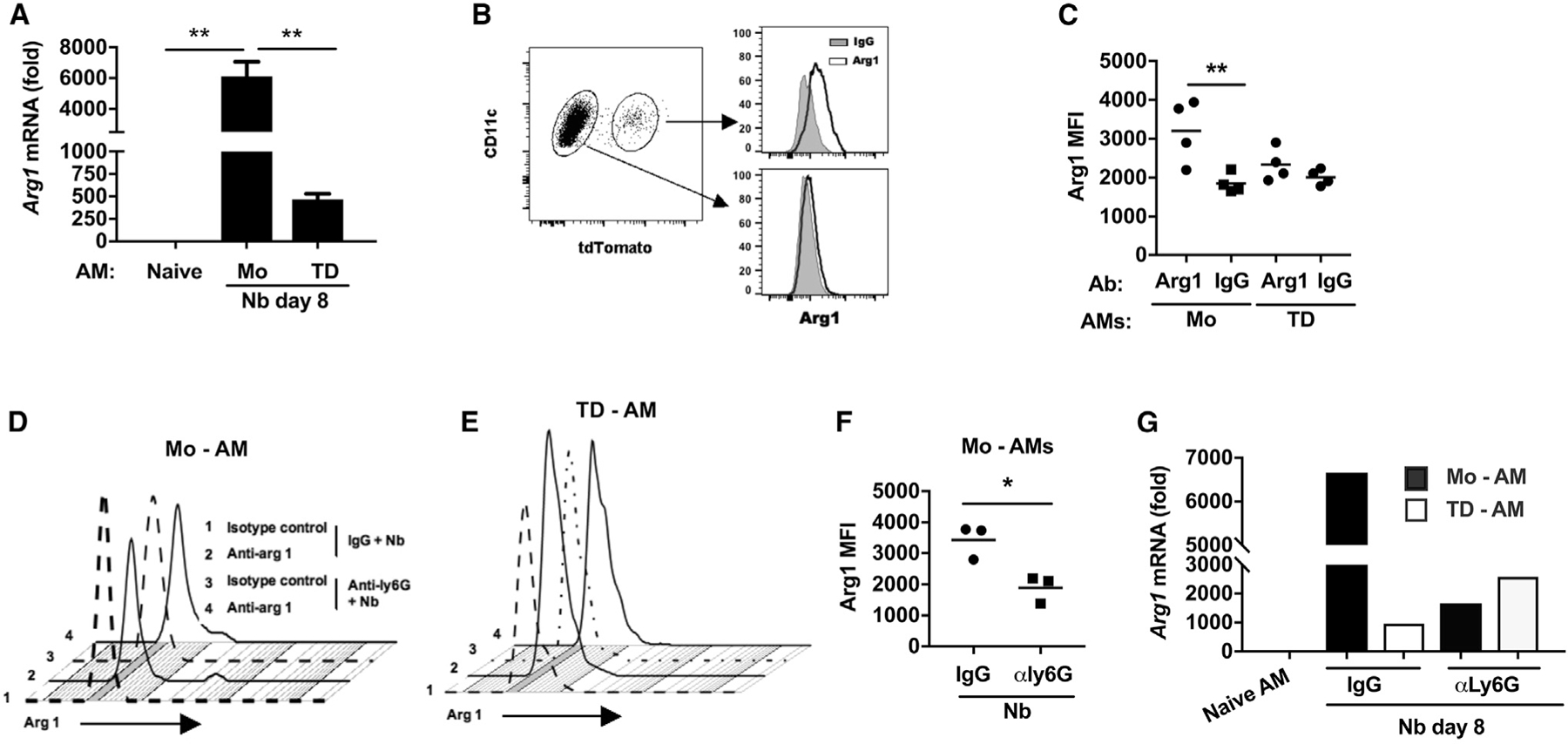
(A–C) Cx3cr1CreERT2-IRES-YFP/+Rosa26floxed-tdTomato/+ reporter mice were administered TAM and inoculated with Nb as described in Figure 5.
(A) Arginase 1 (Arg1) mRNA levels by qPCR in subpopulations of lung AM subsets at day 8 after Nb inoculation expressed relative to naive AMs.
(B and C) Representative flow cytometric analysis of Arg1 intracellular protein expression in AM subsets at day 7 after Nb inoculation (B) and (C) Arg1 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in individual samples from different treatment groups (C).
(D–G) Cx3cr1CreERT2-IRES-YFP/+Rosa26floxed-tdTomato/+ reporter mice were administered anti-Ly6G Ab or isotype control at days −1, 1, and 3 and given TAM at days −1 and +1 after Nb inoculation.
(D and E) Representative flow cytometric analyses of Arg1 intracellular protein expression after neutrophil depletion.
(F) Arg1 MFI in individual samples from each treatment group. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and horizontal lines indicate the mean.
(G) Arg1 mRNA levels by qPCR in macrophage subsets, presented as the fold increase over naive AMs.
Data shown are the mean and SEM of triplicate samples (A) or pooled samples (G) from a total pool of four to eight mice per group. All results are representative of at least two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA).
