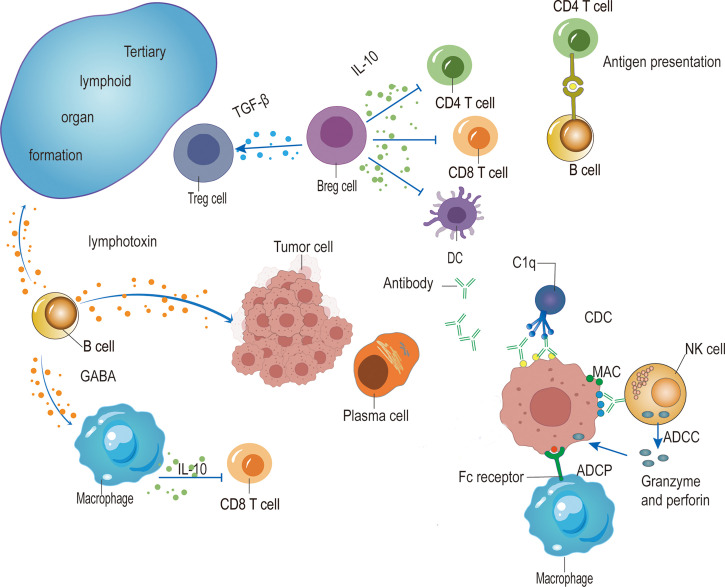
Figure 1.
The role of B cells in tumor immunity. The antibodies produced by plasma cells induce ADCC mediated by NK cells, ADCP by macrophages, and CDC mediated by C1q, which target and kill tumor cells. IgA-expressing Breg cells dampen anti-tumor immunity by secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β to suppress CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and dendritic cells (DCs), and facilitate Treg cells. B cells also promote anti-tumor immunity by presenting antigen to CD4+ T cells and further interacting with activated T cells to induce TFH cells, thus promoting the function of CD8+ T cells. In addition, the production of lymphotoxin from B cells enhances anti-tumor immunity by facilitating tertiary lymphoid organ formation while promoting tumor growth by the induction of angiogenesis. Moreover, B cells produce GABA to impair anti-tumor immunity by facilitating IL-10-producing macrophages.