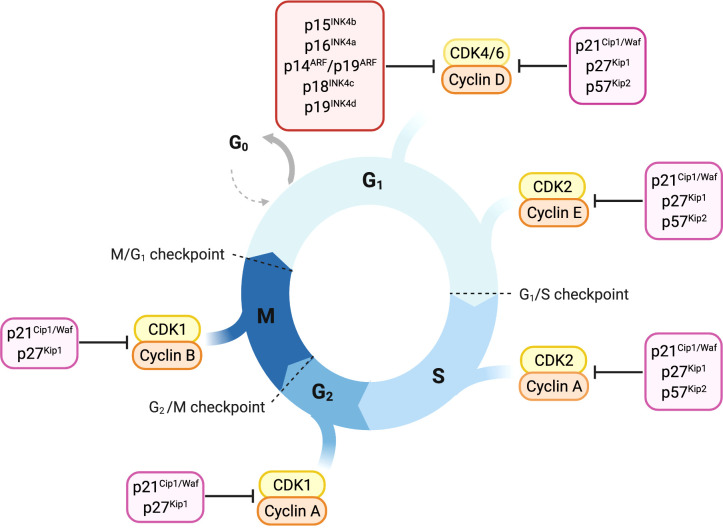
Figure 1.
Overview of cell-cycle control and its main regulators. Progression through cell cycle phases is governed by different CDK-cyclin complexes and the respective cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Members of the INK4 family, p16INK4a, p15INK4b, p18INK4c and p19INK4d, specifically bind and inhibit CDK4/6-cyclin D complexes promoting cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. The Cip/Kip proteins including p21Cip1/Waf, p27kip1 and p57Kip2, play their role as cell-cycle inhibitors by counteracting a broader spectrum of CDK-cyclin complexes. p21Cip1/Waf, p27kip1 and p57Kip2 restrain cell-cycle both during early and late G1 phase by binding either CDK4/6-cyclin D or CDK2-cyclin E complexes. Later in the cell-cycle, they can bind and inhibit CDK2-cyclin A complex, thus imposing a brake during the S-phase. p21Cip1/Waf and p27kip1 are able to delay entry in the M phase by inhibiting CDK1-cyclin A complex and thereby prevent the progression through mitosis counteracting CDK1-cyclin B complex.