Figure 4.
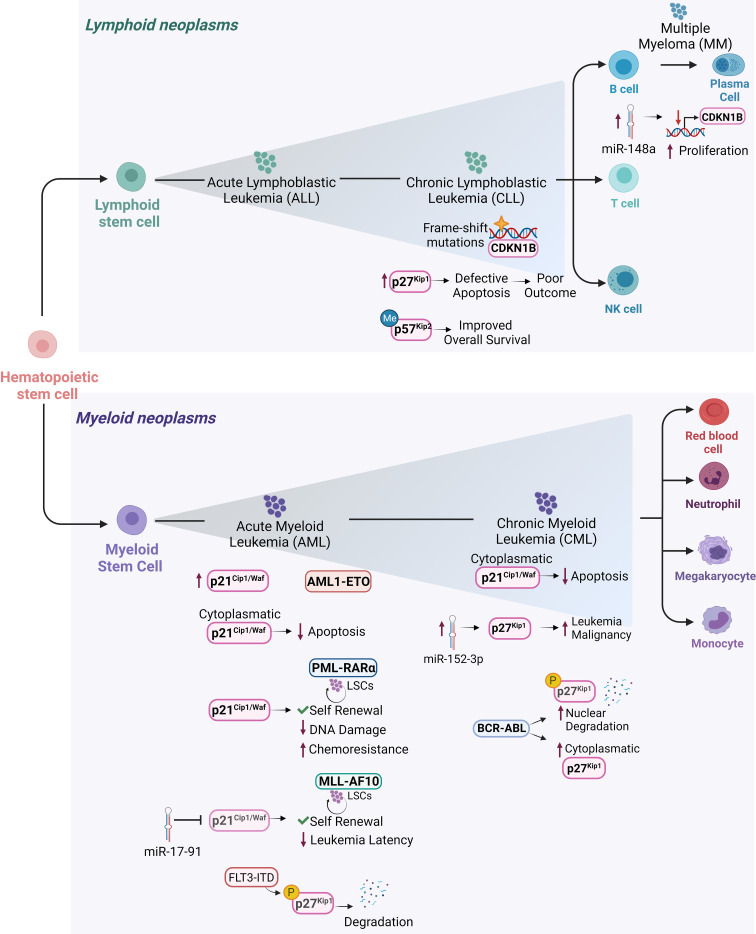
Cip/Kip proteins main deregulations and functions in different hematopoietic malignancies. Schematic representation of the hematopoietic tree and main functions exerted by Cip/Kip proteins in different hematopoietic malignancies. Increased p21Cip1/Waf levels have been reported in AML1-ETO positive AML patients, where it is believed to support LSCs maintenance and self-renewal ability. p21Cip1/Waf anti-apoptotic functions associated with its cytoplasmatic localization have been observed in AML blasts and in cell lines derived from human CML in blast crisis. In PML-RARα LSCs, p21Cip1/Waf expression maintains self-renewal of LSCs and limits DNA damage, thus protecting them from functional exhaustion and conferring chemoresistance. In MLL-AF10 induced AML, p21Cip1/Waf suppression mediated by miR-17-91 leads to decreased leukemia latency. Elevated p27Kip1 levels in B-CLL where they confer protection against apoptosis, are associated with poor outcome. In hairy cell leukemia, a form of B-CLL, CDKN1B gene encoding for p27Kip1 is the second most common altered gene by frame shift mutations. In MM, higher miR-148a levels correlate with decreased CDKN1B expression leading to sustained proliferation. In CML, overexpression of miR-152-3p targets p27Kip1 and promotes leukemia malignancy. In AML, p27Kip1 is subjected to FLT3-ITD phosphorylation (pY88- p27Kip1) which mediates p27Kip1 degradation. BCR-ABL1+ CML can promote degradation of nuclear p27Kip1 and to increased cytoplasmatic p27Kip1, thus compromising p27Kip1 tumor suppressor activity and promoting leukemic cell survival. p57Kip2 gene has been frequently found methylated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients, where the low-risk group it is associated with a more favorable overall survival.