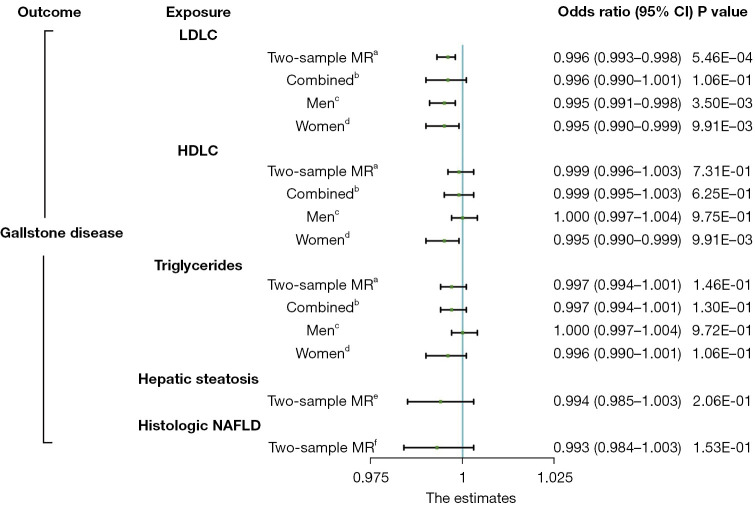
Figure 1.
Comparison of the total causal estimations with heterogeneity and pleiotropic effect between lipid profiles and gallstone disease risk being considered via Mendelian randomization. a, two-sample MR analysis of the Global Lipids Genetics Consortium study and the UK Biobank cohort; b, one-sample MR analysis of all participants in the UK Biobank cohort; c, one-sample MR analysis of male participants in the UK Biobank cohort; d, one-sample MR analysis of female participants in the UK Biobank cohort; e, two-sample MR analysis of the Genetics of Obesity-Related Liver Disease study and the UK Biobank cohort; f, two-sample MR analysis of the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility-Reykjavik study and the UK Biobank cohort. CI, confidence interval; LDLC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDLC, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; MR, Mendelian randomization.