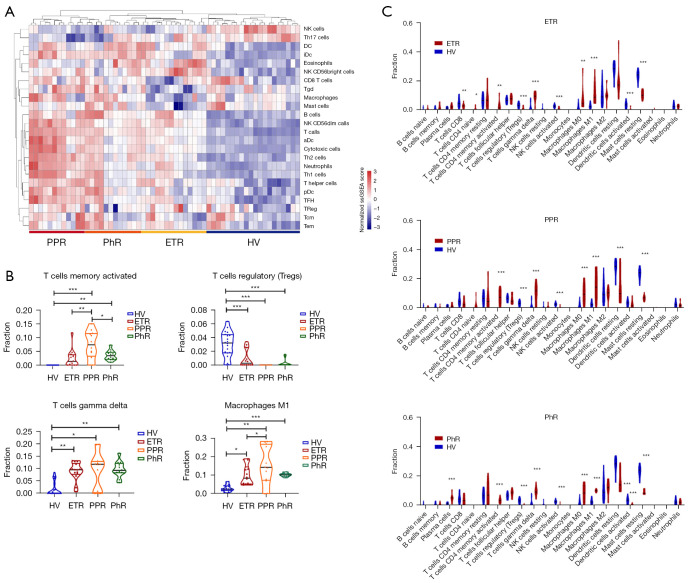
Figure 2.
Immune infiltration analysis of rosacea lesions. (A) A hierarchical clustering heatmap showing the differential infiltration of immune cells between rosacea patients (ETR, PPR, and PhR) and healthy controls. (B) The differential infiltration of activated CD4+ memory T cells, γδ T cells, M1 macrophages, and Treg cells. In three different subtypes of rosacea, activated CD4+ memory T cells, γδ T cells, and M1 macrophages were enriched in rosacea, whereas Treg cells were decreased. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. (C) The differential infiltration of 22 types of immune cells in 3 different subtypes of rosacea. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. PPR, papulopustular rosacea; PhR, phymatous rosacea; ETR, erythematotelangiectatic rosacea; HV, healthy volunteers; NK cells, natural killer cells; Th17 cells, T helper cells 17; DC, dendritic cells; iDc, immature dendritic cells; Tgd, γδ T cells; aDc, activated dendritic cells; Th1 cell, T helper cells 1; Th2 cell, T helper cells 2; pDc, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; TFH, follicular helper T cells; TReg, regulatory T cells; Tcm, central memory T cells; Tem, effective memory T cells.