Table 1.
Key examples of covalent drugs
| Drug (company; former compound name) | Structure | Target | Approvala | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib (AstraZeneca; AZD9291) | 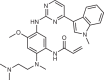 |
Mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor | 2015 for treatment of NSCLC | 44,45,48,49 |
| Ibrutinib (AbbVie; PCI-32765) | 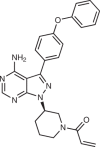 |
BTK inhibitor | 2013 for treatment of mantle-cell lymphoma and, subsequently, many other B cell malignancies | 55,56,60 |
| Sotorasib (Amgen; AMG-510) | 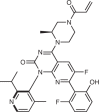 |
KRAS(G12C) inhibitor | 2021 for treatment of NSCLC with KRASG12C mutation | 93–95 |
| Nirmatrelvir (Pfizer; PF-07321332) | 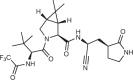 |
SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor | Authorized for emergency use by FDA in 2021 for treatment of COVID-19b | 103,105 |
| Voxelotor (Global Blood Therapeutics; GBT-440) | 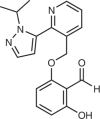 |
Mutant-haemoglobin modulator | 2019 for treatment of sickle cell anaemia | 142,143,145 |
BTK, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. aUnless otherwise indicated, the date of the first approval by one of the major regulatory agencies is provided, which was the FDA in each case. bNirmatrelvir is approved for use in combination with ritonavir (Paxlovid). The FDA’s emergency use authorization preceded approval by other agencies, but Paxlovid has not yet been fully approved by the FDA.
