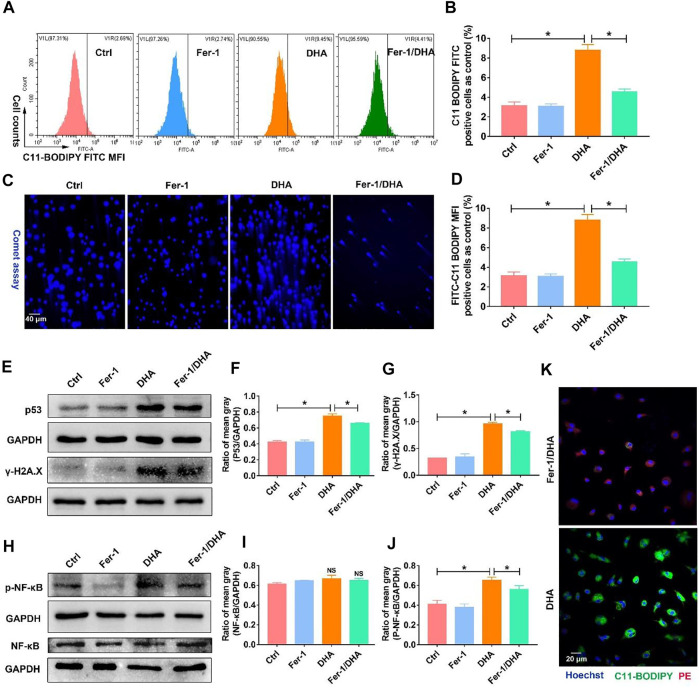
FIGURE 7.
Inhibition of ferroptosis using Fer-1 reduced the DNA damage and activation of NF-κB triggered by DHA. (A,B) The LPO generation, which reflected the ferroptosis of TAM, was assayed using the C11-BODIPY probe. The cellular LPO fluorescence (FITC) was measured through flow cytometry. (C,D) The DDSB was assayed by comet experiments. The comet tail length was counted. (E–G) The expression of p53 and γ-H2A.X, and comet assay were detected to confirm the degree of DNA damage. The results were quantitatively analyzed using mean gray. (H–J) Activation of NF-κB was assayed through the expression of p-NF-κB in TAM. The results were quantitatively analyzed using the mean gray. (K) The LPO generation, which was assayed using the C11-BODIPY probe, was observed by confocal microscopy. Green fluorescence represented LPO accumulation. Values were means ± SD (n = 3, *p < 0.05).