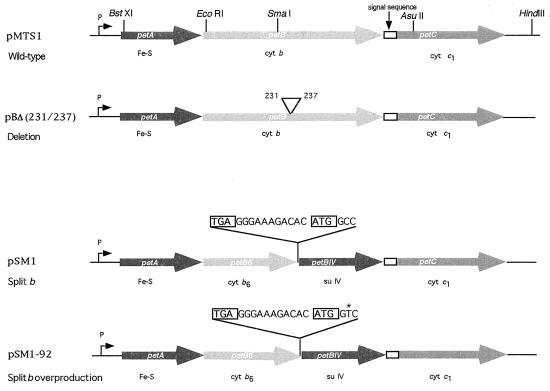
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of petABC(fbcFBC) operon encoding the Fe-S, cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 subunits of R. capsulatus cytochrome bc1 complex. Plasmids pMTS1 and pBΔ(231/237) refer to the wild-type petABC operon and to its variant carrying a deletion in cytochrome b extending from amino acid positions 231 to 237, respectively. Plasmids pSM1 and pSM1-92 correspond to petAB6BIVC derivatives encoding the cytochrome b6c1 complex, obtained after genetically splitting petB into two cistrons (petB6 and petBIV) by introduction of a stop (TGA [boxed]) codon, an intergenic (GGGAAAGACAC) sequence, and a start (ATG [boxed]) codon as indicated. pSM1-92 was derived from pSM1 and contains a single-base-pair substitution at the second base of the second codon of petBIV, as indicated by the asterisk. P and open rectangle, promoter of petABC and processed signal sequence of cytochrome c1, respectively.