Figure 5.
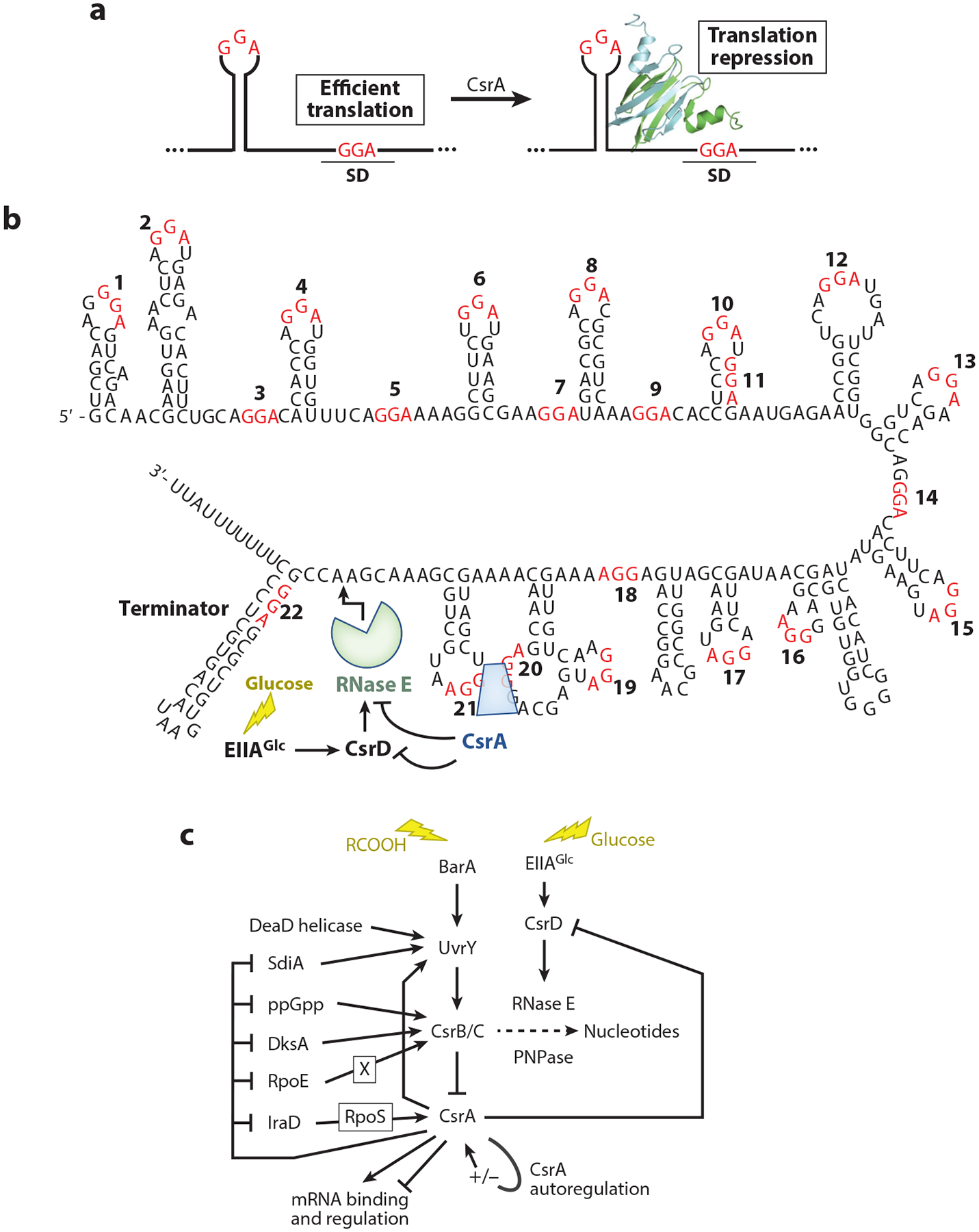
Csr-mediated regulatory pathways. (a) Common CsrA-mediated translation repression mechanism. CsrA dimers, depicted as green and blue ribbons, bind to two sites, one of which overlaps the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence such that bound CsrA blocks ribosome binding. GGA motifs of CsrA-binding sites are in red. (b) CsrB sequence, secondary structure, and RNA-decay pathway. GGA motifs are numbered and shown in red. (c) Circuitry influencing the Csr system. The Csr system of Escherichia coli includes CsrA autoregulation, negative-feedback loops among the Csr components, and reciprocal interactions with other global regulatory systems. Autoregulation and feedback loops fine-tune CsrA activity and support robust regulatory responses, while interactions with other global regulatory systems integrate the Csr system into stress responses. The CsrA ribbon diagram in panel a is adapted with permission from Reference 112.
