Figure 4.
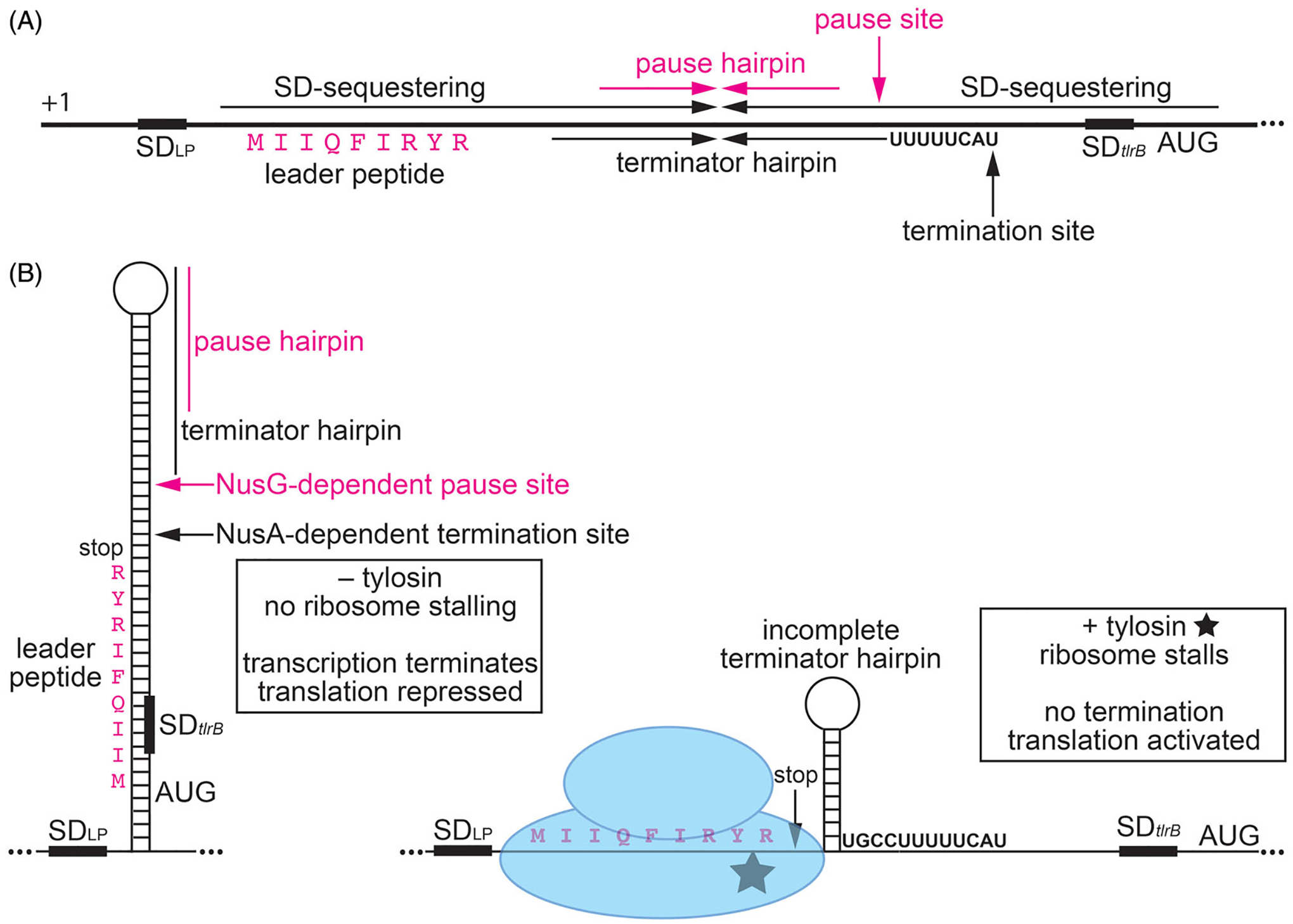
NusG-dependent pausing participates in tylosin-dependent induction of tlrB expression, resulting in antibiotic resistance. The ribosomes translating the leader peptide is simultaneously a sensor of the antibiotic and an effector that effects the structure of the nascent RNA in response to antibiotic challenge. (A) Schematic representation of the tlrB leader region. The thick black line represents the leader region between the start of transcription (+1) and the translation initiation region of tlrB. Inverted repeats for the long SD-sequestering hairpin, terminator hairpin, and pause hairpin (magenta) are labeled. Positions of the NusG-dependent pause site, NusA-dependent termination site, SD sequence (SDLP) for the leader peptide, the leader peptide (magenta), and the SD sequence and AUG start codon for tlrB are also labeled. (B) Model of tylosin-dependent induction of tlrB expression. NusG-dependent RNAP pausing provides time for translation initiation of the leader peptide. In the absence of tylosin (left), the ribosome releases at the stop codon. As a consequence, the terminator hairpin can form and transcription terminates about 50% of the time. For transcripts that fail to terminate, the long tlrB SD-sequestering hairpin forms and represses both tlrB translation and further rounds of leader peptide translation. In the presence of tylosin (right), the ribosome stalls at the C-terminal RYR motif of the leader peptide such that the ribosome remains bound to the nascent transcript. Once RNAP resumes transcription the position of the stalled ribosome prevents completion of the terminator hairpin such that transcription continues into the tlrB coding sequence. The stalled ribosome also prevents the formation of the tlrB SD-sequestering hairpin. Thus, the tlrB SD sequence is single-stranded and translation is activated. TlrB methylates 23S rRNA, leading to tylosin resistance. Color coding is the same as in (A).
