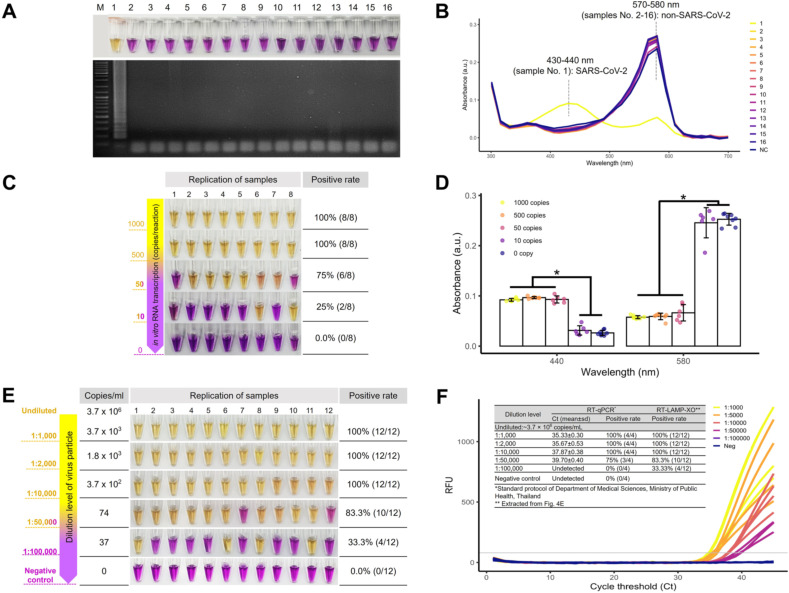
Fig. 3.
Specificity and analytical sensitivity of COVID-19-RT-LAMP-XO for in vitro RNA transcripts and viral RNA isolate. A The molecular specificity of COVID-19-RT-LAMP-XO by the naked-eye observation (top) and AGE (bottom) for (1) SARS-CoV-2 with respect to the following pathogens: (2) Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, (3) Respiratory Syncytial Virus, (4) Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, (5) Influenza A virus subtype H3N2, (6) Influenza B virus (Yamagata lineage), (7) Influenza B virus (Victoria lineage), (8) Influenza B virus (B/Lee/40), (9) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strain AVCT12, (10) Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ATCC 700603, (11) Acinetobacter baumannii strain ATCC 19606, (12) Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain ATCC 27853, (13) Bacillus cereus BCC 6386, (14) Streptococcus pneumoniae, (15) Listeria monocytogenes strain ATCC 19115 and (16) Mycobacterium tuberculosis. B UV–Vis absorption spectra of samples (1)–(16) as shown in A. SARS-CoV-2 positive sample (yellow line) exhibits the peak at 430–440 nm while the remainder of SARS-CoV-2 negative samples exhibits the peak at 570–580 mm that corresponds to the purple hue of the reaction mixture. C The sensitivity of COVID-19-RT-LAMP-XO for in vitro RNA transcripts of the Nsp9 target where the limit of detection was shown to be 500 copies and 50 copies/reaction with a positive rate of 100% and 75%, respectively (N = 8). D UV–Vis absorption measurements at 430–440 nm and 570–580 nm of the colorimetric results shown in C, demonstrating a statistical difference between the positive (POS) and negative outcomes (NEG). E The sensitivity of COVID-19-RT-LAMP-XO for total RNA of the SARS-CoV-2 isolate that was serially diluted down to a factor of 100,000. The limit of detection was shown at 1:10,000 dilution (3.7 × 102 copies/mL-equivalent), which was the last dilution level to achieve a 100% positive rate (N = 12). F Real-time RT-PCR [27] fluorogram of the total RNA isolates shown in E, with summarized sensitivity and cross-comparison with the COVID-19-RT-LAMP-XO results at different dilution levels (inset Table). Both methods showed a comparable detection limit with a 100% positive rate in the Ct ≤ 37.87 ± 0.38 (3.7 × 102 copies/mL-equivalent). M: the DNA marker/ladder. (*, p < 0.00001 Two-Sample t-test). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)