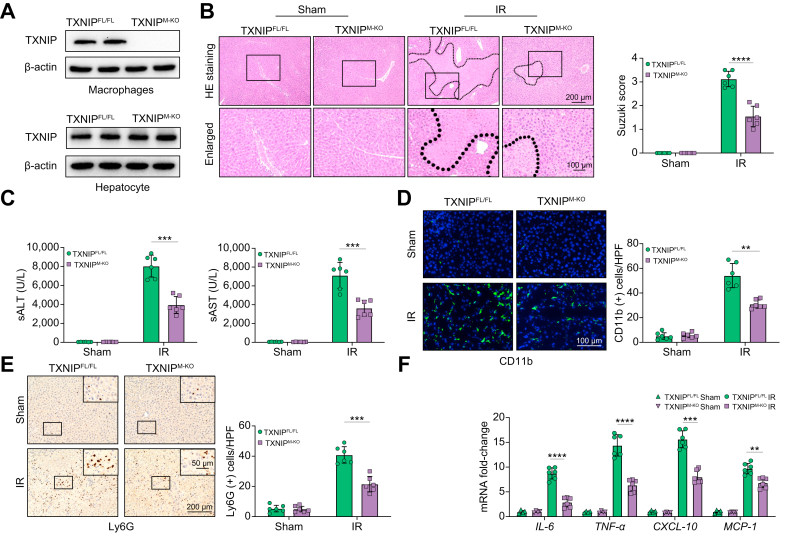
Fig. 1.
Disruption of myeloid-specific TXNIP ameliorates IR-induced liver injury and diminishes macrophage/neutrophil accumulation and proinflammatory mediators in IR-stressed liver.
The TXNIPFL/FL and TXNIPM-KO mice were subjected to 90 min of partial liver warm ischaemia, followed by 6 h of reperfusion. (A) The TXNIP expression was detected in hepatocytes and liver macrophages from IR-stressed livers by Western blot assay. Representative of 4 experiments. (B) Representative histological staining (H&E) of ischaemic liver tissue (n = 6 mice/group) and Suzuki’s histological score. Scale bars, 200 and 100 μm. (C) Liver function in serum samples was evaluated by sALT and sAST levels (IU/L) (n = 6 samples/group). (D) Immunofluorescence staining of CD11b+ macrophages in ischaemic livers (n = 6 mice/group). Quantification of CD11b+ macrophages. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) Immunohistochemistry staining of Ly6G+ neutrophils in ischaemic livers (n = 6 mice/group). Quantification of Ly6G+ neutrophils. Scale bars, 200 and 50 μm. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of IL-6, TNF-α, CXCL-10, and MCP-1 mRNA levels in ischaemic livers (n = 6 samples/group). All data represent the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using the Permutation t test. ∗∗p <0.01. ∗∗∗p <0.005, ∗∗∗∗p <0.001. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CXCL-10, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10; HPF, high power field; IR, ischaemia/reperfusion; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; sALT, serum ALT; sAST, serum AST; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor alpha; TXNIP, thioredoxin-interacting protein; TXNIPFL/FL, floxed TXNIP; TXNIPM-KO, myeloid-specific TXNIP knockout.