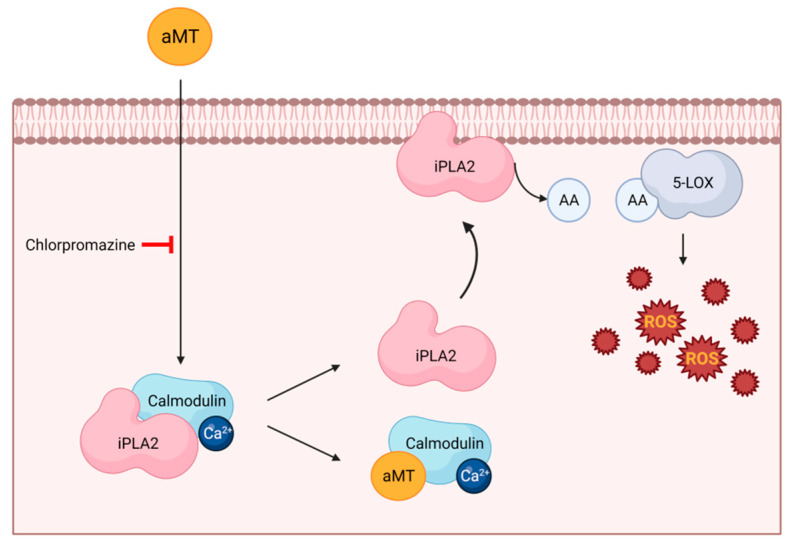
Figure 1.
Melatonin induces ROS production in cancer cells through calmodulin binding. Melatonin binds to calmodulin, leading to the release of sequestered Ca2+-independent PLA2, which is then free to move to membranes and to release high doses of AA; in turn, liberated AA feeds 5-LOX to produce free radicals. Melatonin (aMT); Ca2+-independent PLA2 (iPLA2); arachidonic acid (AA); 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX). Image created using BioRender.com(accessed on 16 July 2022).