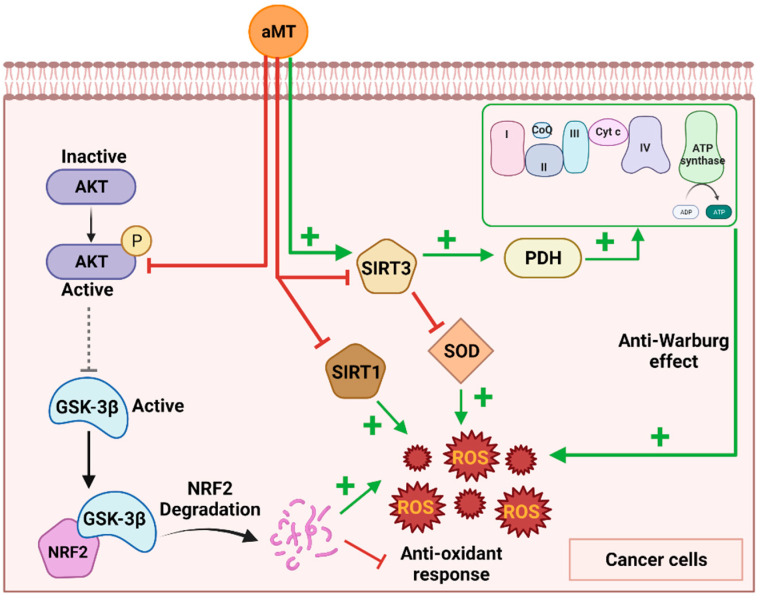
Figure 2.
Different mechanisms by which melatonin induces ROS production in cancer cells. Melatonin inhibits the AKT pathway, leading to the activation of GSK-3β, which induces NRF2 degradation. On the other hand, melatonin regulates Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) through its activation or inhibition, leading to an anti-Warburg effect or SOD inhibition, respectively. Finally, melatonin has been shown to inhibit SIRT1 in cancer cells. All these processes lead to an increase in ROS production and antitumor activity. Melatonin (aMT); glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β); superoxide dismutase (SOD); pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). Image created using BioRender.com (accessed on 18 July 2022).