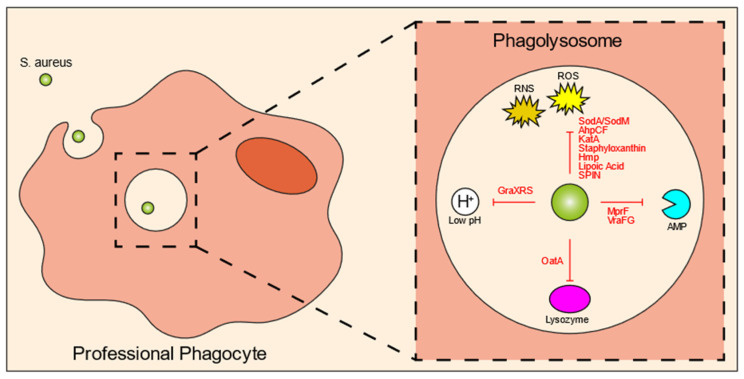
Figure 2.
S. aureus intraphagolysosomal evasion strategies. Once inside the phagolysosome of professional phagocytes, the bacteria get exposed to various antimicrobial molecules designed to kill the bacteria. Co-evolution of host and pathogen has led to a variety of evasion molecules produced by S. aureus to counteract these phagolysosomal killing mechanisms. These mechanisms include evasion molecules against ROS and RNS, AMPs, lysozyme, and acidic pH. Abbreviations: ROS, reactive oxygen species; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; Sod, superoxide dismutase; AhpCF, alkyl hydroperoxidase reductase; KatA, catalase; Hmp, flavohemoglobin; SPIN, staphylococcal peroxidase inhibitor; AMP, antimicrobial peptide; MprF, multiple peptide resistance factor; OatA, O-acetyltransferase.