Table 1.
Evolution of differentiation approaches to generate hPSC-CMs
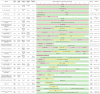 |
Pink cells indicate positive inducers (growth factors, sera, small molecules); yellow cells indicate inhibitors; green cells indicate media and additional supplements used. Acronyms: 2ME, ß-mercaptoethanol; 1TG, monothioglycerol; BIO, 6-bromoindirubin-30-oxime; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; DKK1, Dickkopf-related protein-1; EB, embryoid body; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; END-2, endoderm-like cell line; FBS, fetal bovine serum; FGF2, basic fibroblast growth factor; HF, human fibroblasts; HSA, human serum albumin; ITS, insulin, transferrin, selenium supplement; IWR-1, inhibitor of Wnt response-1; IWP-2, inhibitor of Wnt production 2; IWP-4, inhibitor of Wnt production 4; KO-DMEM, KnockOut DMEM; KSR, KnockOut Serum Replacement; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; MEF-CM, MEF conditioned medium; NEAA, nonessential amino acids; N/S, not stated; PFHM, Protein-Free Hybridoma mixture; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; PVA, polyvinyl alcohol; SCF, stem cell factor; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor.
