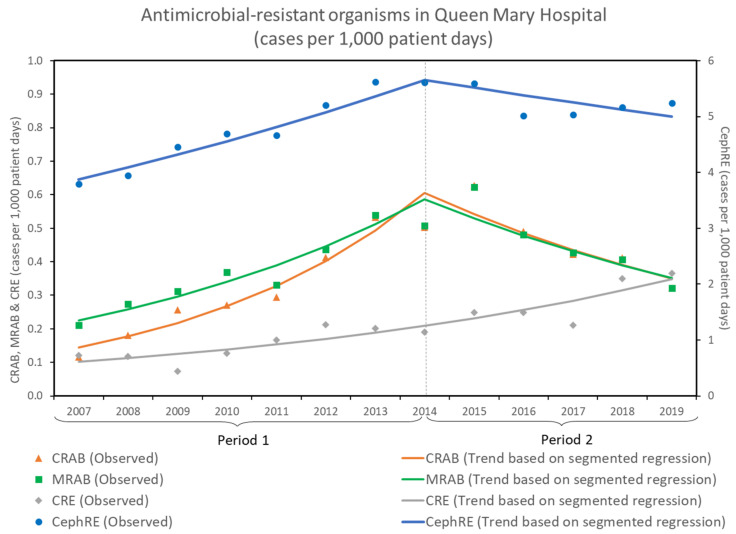
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial-resistant organisms in Queen Mary Hospital from 2007 to 2019. CRAB, carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii; CephRE, cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacterales; CRE, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales; MRAB, multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Remark: CRAB was defined as Acinetobacter baumannii which was non-susceptible (either resistant or intermediate) to either imipenem or meropenem being tested in our microbiology laboratory. MRAB was defined as Acinetobacter baumannii which was non-susceptible (either resistant or intermediate) to at least one agent in at least 3 antimicrobial classes of aminoglycosides, extended spectrum BLBI combination, carbapenems, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and sulbactam [41]. CRE was defined as the microorganisms (E. coli, Klebsiella species, and Enterobacter species), under the order of Enterobacterales commonly cause infections in healthcare settings, non-susceptible (either resistant or intermediate) to either imipenem or meropenem [43]. CephRE was defined as the microorganisms (E. coli, Klebsiella species, and Enterobacter species) non-susceptible (either resistant or intermediate) to either cefepime, ceftazidime, or ceftriaxone in this study.