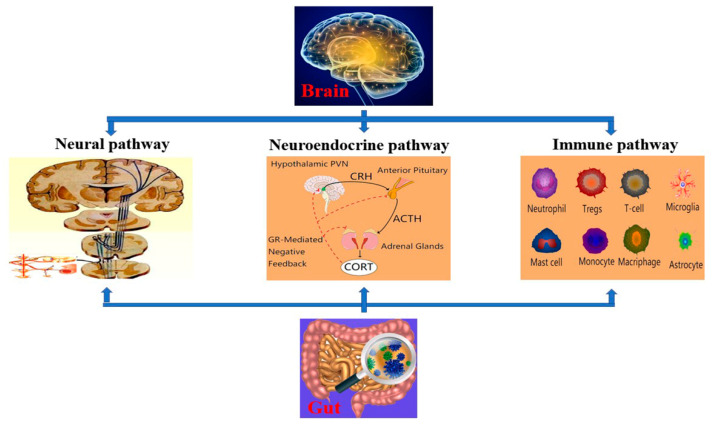
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the 3 pathways (neural, neuroendocrine and immune) that constitute the brain–gut axis. (1). Neural pathway: the brain regulates gut function mainly through ANS, while the gut microbiome exerts a feedback effect on the brain. (2). Neuroendocrine pathway: stimulation of the brain is transmitted to the gut via the HPA axis, while the gut microbiome influences the brain by affecting the production of immune mediators to activate the HPA axis. (3). Immune pathway: the brain causes gut dysfunction via releasing proinflammatory cytokines to recruit other immune cells, while the gut microbiome disrupts BBB integrity by downregulating TJs expression.