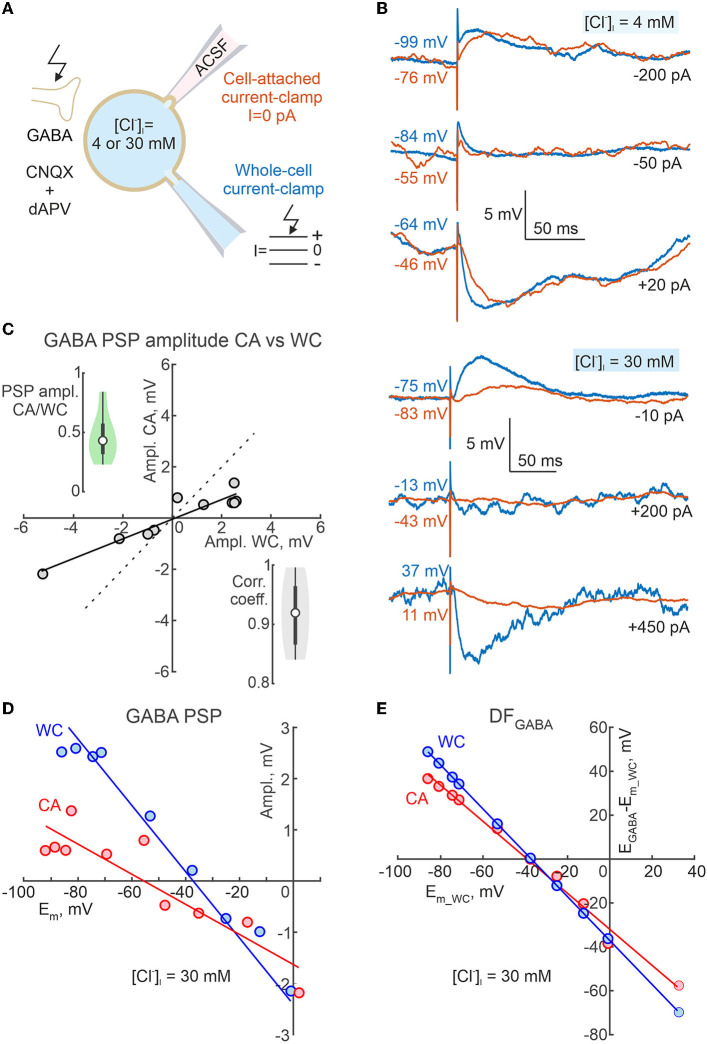
Figure 9.
Dependence of the polarity of GABA-PSPs during cell-attached current clamp recordings on neuronal membrane potential and intracellular chloride. (A) Scheme of the experimental setup. Dual CA and WC current-clamp recordings of the pharmacologically isolated, electrically evoked GABA-PSPs were performed from adolescent CA1 pyramidal cells at different Em values imposed by current injection into the WC electrode, and at various [Cl−]i (4 mM and 30 mM) in the WC pipette solution. Ionotropic glutamate receptors were blocked by CNQX (10 μM) and d-APV (40 μM). (B) Examples of evoked GABA-PSPs during concomitant CA and WC recordings with [Cl−]i = 4 mM (top traces) and 30 mM (bottom traces) in the WC pipette at different membrane potentials. (C) Relationships between amplitudes of evoked GABA-PSPs in WC and CA configurations for a cell shown on (B) with [Cl−]i = 30 mM. The points represent the average of 10 GABA-PSP recorded at different Em_wc values. Note that GABA-PSPs in WC and CA have similar polarity and that the conductance of GABA-PSPs in CA is smaller than in WC. The insets show group data on the CA/WC transfer coefficient of GABA-PSP amplitude (top left) and the correlation coefficient between GABA-PSP amplitude in CA and WC (bottom right) (n = 8 CA1 pyramidal cells from P15-19 mice). (D) Dependence of GABA-PSPs amplitude in WC and CA recordings on Em_wc and Em_ca, respectively for a CA1 pyramidal neuron recorded with [Cl−]i = 30 mM in the WC pipette solution. The Em scale is the same for Em_wc and Em_ca. (E) Dependence of DFGABA relative Em_wc for GABA-PSPs recorded in CA and WC for a cell shown on (D).