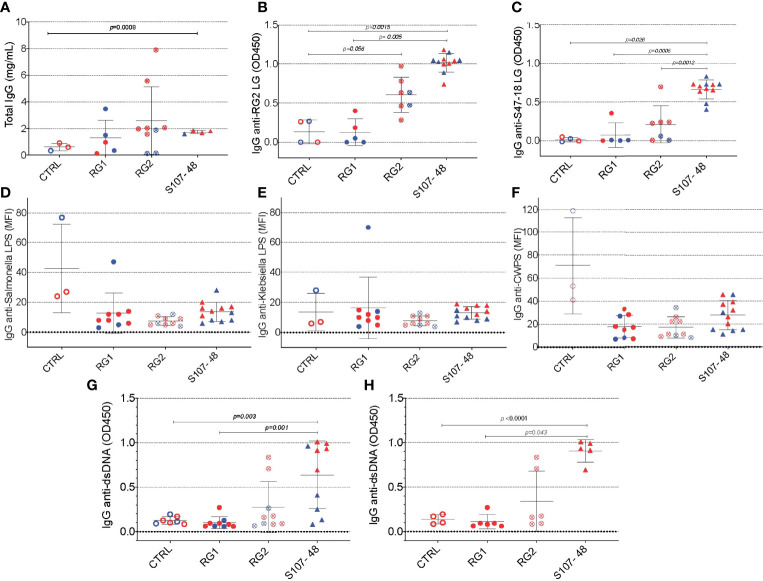
Figure 6.
Intestinal colonization with certain RG strains induces IgG RG strain-associated cell wall lipoglycan antibodies and anti-native DNA autoantibodies. (A) Following neonatal colonization of litters from RG colonized GF breeding pairs, S107-48 RG strain colonized mice display numerically higher mean serum total IgG levels, compared to controls. (B) Neonatal colonization with the RG2 strain or with the S107-48 RG strain induced significantly raised serum levels of IgG anti-RG2 strain cell wall lipoglycan antibodies. (C) Neonatal RG colonization does not induce raised IgG-antibody levels to; (D) Salmonella LPS, (E) Klebsiella LPS, or (F) to pneumococcal cell wall polysaccharide (CWPS). (G) Neonatal colonization with the S107-48 RG strain induces raised serum levels of IgG anti-native DNA autoantibodies. (H) Elevation of IgG anti native DNA following neonatal S107-48 RG strain was greatest in the female mice. (n= 4 to 11 per group). Antibody assays for IgG anti-native DNA used plasma diluted at 1:100 in ELISA (OD450). Antibody assays for IgG antibodies to RG lipoglycans, LPS and CWPS were performed by bead-based multiplex array (MFI) with plasma diluted 1:1000. Comparisons by unpaired t test, p values shown.