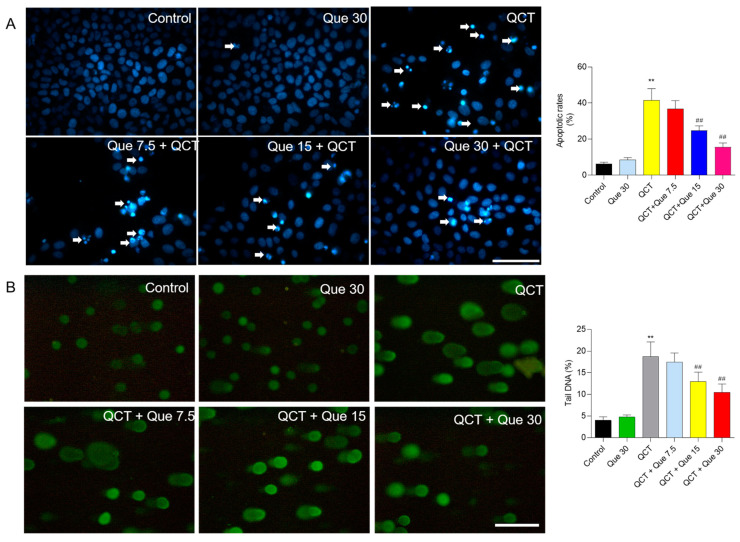
Figure 3.
The effect of quercetin supplementation on QCT-induced cell apoptosis and DNA damage in human L02 cells. (A), the representative images of cell apoptosis and the results of quantitative analysis. L02 cells were treated with quercetin pretreatment at concentrations of 7.5, 15, and 30 μM for 2 h, followed by co-treatment with QCT at a final concentration of 5 μg/mL for an additional 24 h, and cell apoptosis was stained with Hoechst 33342. Finally, the representative images were obtained using the fluorescence microscope (on the left) and apoptotic rates were quantified using Image J (on the right). The white arrowheads indicate the apoptotic cells. (B), the results of the comet assay. L02 cells were pretreated with quercetin at final concentrations of 7.5, 15, and 30 μM for 2 h, followed by co-treatment with QCT at a final concentration of 5 μg/mL for 4 h, and the comet assay was performed. The representative images were obtained using the fluorescence microscope (on the left) and the percentage (%) of tail DNA was quantified (on the right). All results were presented as mean ± SD (n = 4 independent experiments). ** p < 0.01, compared to the vehicle control group; ## p < 0.01, compared to the QCT-alone group. QCT, quinocetone; Que, quercetin; Bar = 50 μm.