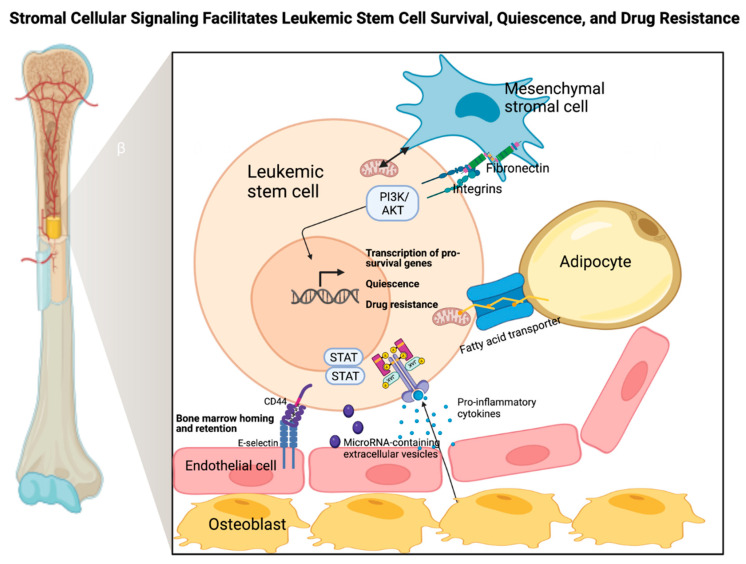
Figure 1.
Stromal cellular signaling facilitates leukemic stem cell (LSC) survival, quiescence, and drug resistance. LSCs engage in bidirectional crosstalk with multiple BM cellular constituents. E-selectin expressed on the surface of endothelial cells interacts with CD44 on LSCs to drive LSC homing and retention in the protective BM microenvironment, sheltering LSCs from therapeutic insults. Furthermore, endothelial cells also release microRNA (miRNA)-containing extracellular vesicles to further enrich the quiescence phenotype of LSCs. Osteoblasts primarily release proinflammatory cytokines that lead to the transcription of genes implicated in LSC survival, self-renewal, and quiescence. Mesenchymal stromal cells are known to physically transfer mitochondria to LSCs via nanotubes to repair and replace damaged mitochondria with new ones inside LSCs, potentially helping LSCs evade apoptosis. Mesenchymal stromal cells can also activate pro-survival integrin-mediated signaling in LSCs, involving the PI3K/AKT pathway. Moreover, adipocytes assist in the rewiring of LSC metabolism, supplying free fatty acids to fuel oxidative phosphorylation, a known metabolic dependency of LSCs.